SECTION 100-04: Noise, Vibration and Harshness | 2002 Escape Workshop Manual |
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING | Procedure revision date: 06/14/2001 |
Noise, Vibration And Harshness (NVH)
Special Tool(s)
 | ChassisEAR
107-R2102 or equivalent |
 | Vibration Analyzer
100-F027 (014-00344) or equivalent |
 | EngineEAR
107-R2100 or equivalent |
 | Ultrasonic Leak Detector
134-R0135 or equivalent |
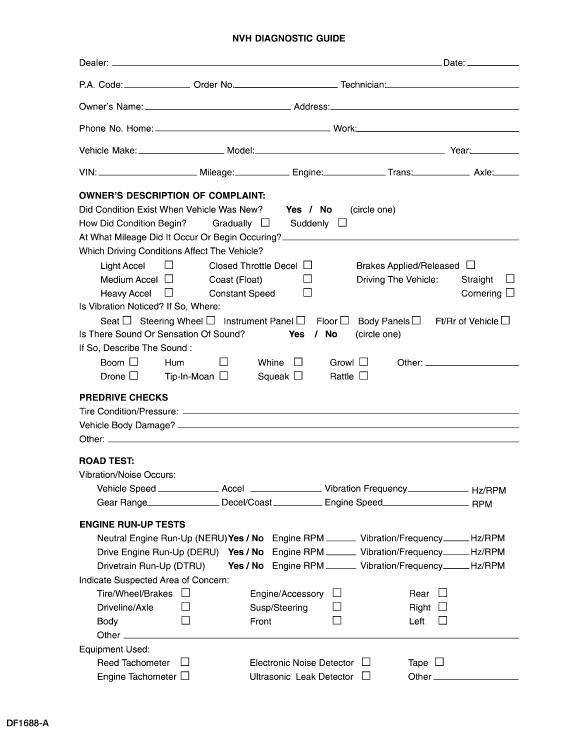
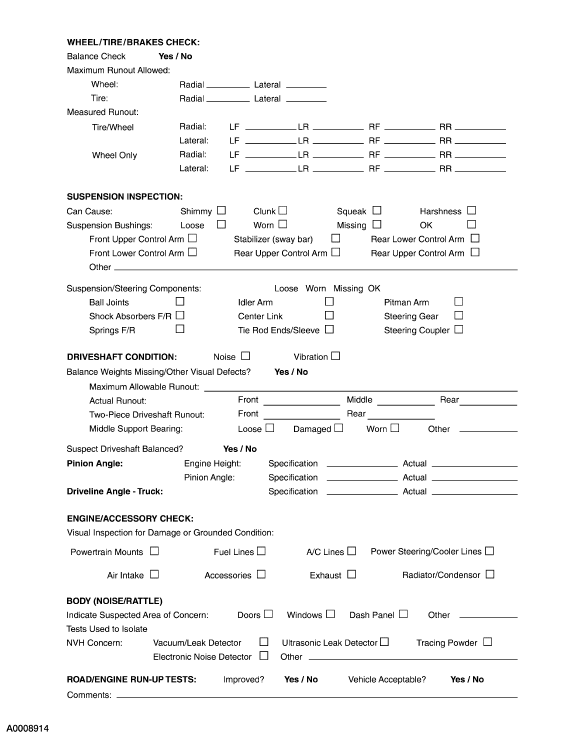
To assist the service advisor and the technician, a Write-up Job Aid and an NVH Diagnostic Guide are included with this material. The Write-up Job Aid serves as a place to record all important symptom information. NHV Diagnostic Guide serves as a place to record information reported on the Write-up Job Aid as well as data from the testing to be carried out.
To begin a successful diagnosis, fill out the NVH Diagnostic Guide, record the reported findings, then proceed to each of the numbered process steps to complete the diagnosis.
1: Customer Interview
The diagnostic process starts with the customer interview. The service advisor must obtain as much information as possible about the concern and take a test drive with the customer. There are many ways a customer will describe NVH concerns and this will help minimize confusion arising from descriptive language differences. It is important that the concern is correctly interpreted and the customer descriptions are recorded. During the interview, ask the following questions:
- When was the concern first noticed?
- Did the concern appear suddenly or gradually?
- Did any abnormal occurrence coincide with or proceed its appearance?
Use the information gained from the customer to accurately begin the diagnostic process.
2: Pre-Drive Check
It is important to do a pre-drive check before road testing the vehicle. A pre-drive check verifies that the vehicle is relatively safe to drive and eliminates any obvious faults on the vehicle.
The pre-drive check consists of a brief visual inspection. During this brief inspection, take note of anything that will compromise safety during the road test and make those repairs or adjustments before taking the vehicle on the road.
3: Preparing for the Road Test
Observe the following when preparing for the road test:
- Review the information recorded on the NVH Diagnostic Guide. It is important to know the specific concern the customer has with the vehicle.
- Do not be misled by the reported location of the noise or vibration. The cause can actually be some distance away, transferred from another part of the vehicle.
- Remember that the vibrating source component (originator) may only generate a small vibration. This small vibration can in turn cause a larger vibration or noise to emanate from another receiving component (reactor), due to contact with other components (transfer path).
- Conduct the road test on a quiet street where it is safe to duplicate the vibration or noise. The ideal testing route is an open, low-traffic area where it is possible to operate the vehicle at the speed in which the condition occurs.
- If possible, lower the radio antenna in order to minimize turbulence. Identify anything that could potentially make noise or be a source of wind noise. Inspect the vehicle for add-on items that create vibration/noise. Turn off the radio and the heating and cooling system blower.
- The engine speed is an important factor in arriving at a final conclusion. Therefore, connect an accurate tachometer to the engine, even if the vehicle has a tachometer. Use a tachometer that has clearly defined increments of less than 50 rpm. This ensures an exact engine speed reading.
4: Verify the Customer Concern
Verify the customer concern by carrying out a road test, an engine run-up test, or both.
The decision to carry out a road test, an engine run-up test, or both depends on the type of NVH concern. A road test may be necessary if the symptom relates to the suspension system or is sensitive to torque. A drive engine run-up (DERU) or a neutral engine run-up (NERU) test identifies noises and vibrations relating to engine and drivetrain rpm. Remember, a condition will not always be identifiable by carrying out these tests, however, they will eliminate many possibilities if carried out correctly.
5: Road Test
NOTE: It may be necessary to have the customer ride along or drive the vehicle to point out the concern. During the road test, take into consideration the customer's driving habits and the driving conditions. The customer's concern just may be an acceptable operating condition for that vehicle.
The following is a brief overview of each test in the order in which it appears. A review of this information helps to quickly identify the most appropriate process necessary to make a successful diagnosis. After reviewing this information, select and carry out the appropriate test(s), proceeding to the next step of this process.
- The Slow Acceleration Test is normally the first test to carry out when identifying an NVH concern, especially when a road test with the customer is not possible.
- The Heavy Acceleration Test helps to determine if the concern is torque-related.
- The Neutral Coast Down Speed Test helps to determine if the concern is vehicle speed-related.
- The Downshift Speed Test helps to determine if the concern is engine speed-related.
- The Steering Input Test helps to determine how the wheel bearings and other suspension components contribute to a vehicle speed-related concern.
- The Brake Test helps to identify vibrations or noise that are brake-related.
- The Road Test Over Bumps helps isolate a noise that occurs when driving over a rough or bumpy surface.
- The Engine Run-Up Tests consist of the Neutral Run-up Test and the Engine Load Test. These tests help to determine if the concern is engine speed-related.
- The Neutral Run-up Test is used as a follow-up test to the Downshift Speed Test when the concern occurs at idle.
- The Engine Load Test helps to identify vibration/noise sensitive to engine load or torque. It also helps to reproduce engine speed-related concerns that cannot be duplicated when carrying out the Neutral Run-up Test or the Neutral Coast Down Test.
- The Engine Accessory Test helps to locate faulty belts and accessories that cause engine speed-related concerns.
- The Vehicle Cold Soak Procedure helps to identify concerns occurring during initial start-up and when an extended time lapse occurs between vehicle usage.
Slow Acceleration Test
To carry out this test, proceed as follows:
- Slowly accelerate to the speed where the reported concern occurs. Note the vehicle speed, the engine rpm and, if possible, determine the vibration frequency.
- Attempt to identify from what part of the vehicle the concern is coming.
- Attempt to identify the source of the concern.
- Proceed as necessary.
Heavy Acceleration Test
To carry out this test, proceed as follows:
- Accelerate hard from 0-64 km/h (0-40 mph).
- Decelerate in a lower gear.
- The concern is torque-related if duplicated while carrying out this test.
- Proceed as necessary.
Neutral Coast Down Speed Test
To carry out this test, proceed as follows:
- Drive at a higher rate of speed than where the concern occurred when carrying out the Slow Acceleration Test.
- Place the transmission in NEUTRAL and coast down past the speed where the concern occurs.
- The concern is vehicle speed-related if duplicated while carrying out this test. This eliminates the engine and the torque converter as sources.
- If the concern was not duplicated while carrying out this test, carry out the Downshift Speed Test to verify if the concern is engine speed-related.
- Proceed as necessary.
Downshift Speed Test
To carry out this test, proceed as follows:
- Shift into a lower gear than the gear used when carrying out the Slow Acceleration Test.
- Drive at the engine rpm where the concern occurs.
- The concern is engine speed related if duplicated while carrying out this test. This eliminates the tires, wheels, brakes and the suspension components as sources.
- If necessary, repeat this test using other gears and NEUTRAL to verify the results.
- Proceed as necessary.
Steering Input Test
To carry out this test, proceed as follows:
- Drive at the speed where the concern occurs, while making sweeping turns in both directions.
- If the concern goes away or gets worse, the wheel bearings, hubs, U-joints (contained in the axles of 4WD applications), and tire tread wear are all possible sources.
- Proceed as necessary.
Brake Test
To carry out this test, proceed as follows:
- Warm the brakes by slowing the vehicle a few times from 80–32 km/h (50–20 mph) using light braking applications. At highway speeds of 89–97 km/h (50–60 mph), apply the brake using a light pedal force.
- Accelerate to 89–97 km/h (55–60 mph).
- Lightly apply the brakes and slow the vehicle to 30 km/h (20 mph).
- A brake vibration noise can be felt in the steering wheel, seat or brake pedal. A brake noise can be heard upon brake application and diminish when the brake is release.
Road Test Over Bumps
To carry out this test, proceed as follows:
- Drive the vehicle over a bump or rough surface one wheel at a time to determine if the noise is coming from the front or the back and the left or the right side of the vehicle.
- Proceed as necessary.
Neutral Engine Run-up (NERU) Test
To carry out this test, proceed as follows:
- Install a tachometer.
- Increase the engine rpm up from an idle to approximately 3,500 rpm while in PARK on front wheel drive vehicles with automatic transmissions, or NEUTRAL for all other vehicles. Note the engine rpm and, if possible, determine the vibration frequency.
- Attempt to identify what part of the vehicle the concern is coming from.
- Attempt to identify the source of the concern.
- Proceed as necessary.
Drive Engine Run-Up (DERU) Load Test
To carry out this test, proceed as follows:
 WARNING: Block the front and rear wheels, and apply the parking brake and the service brake, or injury to personnel can result.
WARNING: Block the front and rear wheels, and apply the parking brake and the service brake, or injury to personnel can result.
 CAUTION: Do not carry out the Engine Load Test for more than five seconds or damage to the transmission or transaxle can result.
CAUTION: Do not carry out the Engine Load Test for more than five seconds or damage to the transmission or transaxle can result.
Block the front and rear wheels.- Apply the parking brake and the service brake.
- Install a tachometer.
- Shift the transmission into DRIVE, and increase and decrease the engine rpm between an idle to approximately 2,000 rpm. Note the engine rpm and, if possible, determine the vibration frequency.
- Repeat the test in REVERSE.
- If the vibration or noise is duplicated when carrying out this test, inspect the engine and transmission or transaxle mounts.
- If the concern is definitely engine speed-related, carry out the Engine Accessory Test to narrow down the source.
- Proceed as necessary.
Engine Accessory Test
To carry out this test, proceed as follows:
 WARNING: Block the front and rear wheels, and apply the parking brake and the service brake, or injury to personnel can result.
WARNING: Block the front and rear wheels, and apply the parking brake and the service brake, or injury to personnel can result.
 CAUTION: Limit engine running time to one minute or less with belts removed or serious engine damage will result.
CAUTION: Limit engine running time to one minute or less with belts removed or serious engine damage will result.
NOTE: A serpentine drive belt decreases the usefulness of this test. In these cases, use a vibration analyzer, such as the EVA, to pinpoint accessory vibrations. An electronic listening device, such as an EngineEAR, will also help to identify noises from specific accessories.
Remove the accessory drive belts.- Increase the engine rpm to where the concern occurs.
- If the vibration/noise is duplicated when carrying out this test, the belts and accessories are not sources.
- If the vibration/noise was not duplicated when carrying out this test, install each accessory belt, one at a time, to locate the source.
Vehicle Cold Soak Procedure
To carry out this procedure, proceed as follows:
6: Check OASIS/TSBs/Repair History
After verifying the customer concern, check for OASIS reports, TSBs and the vehicle repair history for related concerns. If information relating to a diagnosis/repair is found, carry out the procedure(s) specified in that information.
If no information is available from these sources, carry out the vehicle preliminary inspection to eliminate any obvious faults.
7: Diagnostic Procedure
Qualifying the concern by the particular sensation present can help narrow down the concern. Always use the "symptom" to "system" to "component" to "cause" diagnosis technique. This diagnostic method divides the problem into related areas to correct the customer concern.
- Verify the "symptom".
- Determine which "system(s)" can cause the "symptom".
- If a vibration concern is vehicle speed related, the tire and wheel rpm/frequency or driveshaft frequency should be calculated.
- If a vibration concern is engine speed related, the engine, engine accessory or engine firing frequencies should be calculated.
- After determining the "system", use the diagnostic tools to identify the worn or damaged "components".
- After identifying the "components", try to find the "cause" of the failure.
Once the concern is narrowed down to a symptom/condition, proceed to NVH Condition and Symptom Categories.
NVH Condition and Symptom Categories
Operating Condition—Vehicle is Not Moving
- Static operation
- While cranking
- Grinding or whine, differential ring gear or starter motor pinion noise. GO to Symptom Chart — Engine Noise/Vibration.
- Rattle. Exhaust hanger, exhaust heat shield or A/C line noise. GO to Symptom Chart — Squeak and Rattle.
- Vibration. Acceptable condition.
- At idle
- During gear selection
- Vehicle parked on a steep incline. Acceptable noise.
- Vehicle parked on a flat surface. GO to Symptom Chart — Driveline Noise/Vibration.
- Vehicle with a manual transmission. GO to Symptom Chart — Transmission (Manual) and Transfer Case Noise/Vibration.
Operating Condition—Vehicle is Moving
- Depends more on how the vehicle is operated
- Speed-related
- Related to vehicle speed
- Related to engine speed.
- Acceleration
- Wide open throttle (WOT)
- Engine induced contact between components. Inspect and repair as necessary.
- Noise is continuous throughout WOT. Exhaust system or engine ground out. GO to Symptom Chart — Engine Noise/Vibration.
- Light/moderate acceleration
- Turning noise. GO to Symptom Chart —Steering Noise/Vibration.
- Braking.
- Clutching.
- Shifting
- Engaged in four-wheel drive. GO to Symptom Chart — Transmission (Manual) and Transfer Case Noise/Vibration.
- Cruising speeds
- Driving at low/medium speeds
- Depends more on where the vehicle is operated
- Bump/pothole, rough road or smooth road. GO to Symptom Chart — Suspension Noise/Vibration.
Symptom Charts
Symptom Chart—Brake Noise/Vibration
| Condition | Possible Sources | Action |
|---|
| - Caliper mounting bolts loose.
| - CHECK the caliper bolts. TIGHTEN to specifications. REFER to Section 206-03.
|
| - Damaged or worn caliper pins or retainers.
| - CHECK the caliper pins and retainers for lubrication and correct fit. LUBRICATE or INSTALL new components as necessary.
|
| - Missing or damaged anti-rattle clips or springs.
| - CHECK the brake pads for missing clips or broken springs. INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 206-03.
|
| | - TIGHTEN the brake disc shield bolts to specification. REFER to Section 206-03.
|
- Clicking noise—with brakes applied with ABS brakes
| - ABS hydraulic control unit.
| |
- Squealing noise—occurs on first (morning) brake application
| | - Acceptable condition. Caused by humidity and low disc brake pad temperature.
|
- Squealing noise—a continuous squeal
| - Disc brake pads worn below minimum thickness.
| |
- Squealing noise—an intermittent squeal brought on by cold, heat, water, mud or snow
| | |
- Groaning noise—occurs at low speeds with brake lightly applied (creeping)
| | |
- Grinding noise—continuous
| - Disc brake pads worn below minimum thickness.
| - INSPECT the brake pads, shoes, brake discs/drums and attaching hardware for damage. REPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 206-03 for front disc brakes or Section 206-02 for drum brakes.
|
| - Brake linings contaminated with grease or oil.
| - INSPECT the brake pads and shoes for contamination. REPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 206-03 for front disc brakes or Section 206-02 for rear drum brakes.
|
- Brake vibration/shudder—occurs when brakes are applied
| - Uneven disc or drum wear.
- Uneven disc brake pad or lining transfer.
- Suspension components.
| |
- Brake vibration/shudder—occurs when the brake pedal is released
| | - INSPECT the brake pads and shoes for premature wear. REPAIR or INSTALL a new caliper or wheel cylinder as necessary. REFER to Section 206-03 for front disc brakes or Section 206-02 for rear drum brakes.
|
Symptom Chart—Driveline Noise/Vibration
| Condition | Possible Sources | Action |
|---|
- Axle howling or whine—rear axle or transfer case
| | - CHECK the lubricant level. FILL the axle to specification.
|
| | - INSPECT the axle housing for damage. REPAIR or INSTALL a new axle as necessary. REFER to Section 205-02.
|
| - Damaged or worn wheel bearings or axle bearings.
| |
| - Damaged or worn differential ring and pinion.
| - INSPECT the ring and pinion ring for abnormal wear patterns or broken teeth. INSTALL a new ring and pinion as necessary. REFER to Section 205-02.
|
| - Damaged or worn differential side or pinion bearings.
| - CHECK for abnormal bearing play or roughness. INSTALL new bearings as necessary. REFER to Section 205-02.
|
| - Damaged or worn differential side gears and pinion gears.
| - DISASSEMBLE the differential carrier. INSPECT the side and pinion gears for abnormal wear patterns or broken teeth. INSTALL new gears as necessary. REFER to Section 205-02.
|
| - Transfer case housing or internal gear damage or low lubricant.
| - INSPECT the transfer case for damage. CHECK the lubricant level and fill transfer case to specification. REFER to Section 308-07B.
|
- Driveline clunk—loud clunk when shifting from reverse to drive
| - Incorrect axle lubricant level.
| - CHECK the lubricant level. FILL the axle to specification.
|
| - Excessive backlash in the axle or transmission.
| - CARRY OUT a total backlash check.
|
| - Damaged or worn pinion bearings.
| - CHECK for abnormal bearing play or roughness. INSTALL new bearings as necessary. REFER to Section 205-02.
|
| - Damaged or worn universal joints (U-joints).
| - INSPECT the U-joints for wear or damage. INSTALL new U-joints as necessary. REFER to Section 205-01.
|
| - Loose suspension components.
| - INSPECT the suspension for damage or wear. REPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 204-00.
|
| - Broken powertrain mounts.
| - INSPECT the powertrain mounts. INSTALL new mounts as necessary. REFER to Section 303-01A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-01B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
| | - CHECK for the correct idle speed.
|
- Driveline clunk—occurs as the vehicle starts to move forward following a stop
| - Worn driveshaft constant velocity (CV) joint or U-joints with excessive play.
| - INSPECT the CV joint and U-joints for a worn condition. INSTALL a new Driveshaft as necessary. REFER to Section 205-01.
|
| | - CHECK the axle for loose bolts. TIGHTEN to specification.
|
- Driveline clunk (FWD vehicles)—occurs during acceleration or from cruise to coast/deceleration
| - Damaged or worn inboard CV joint.
| - INSPECT the inboard CV joint and boot. REPAIR or INSTALL a new CV joint as necessary. REFER to Section 205-04.
|
- Driveline clunk (4WD vehicles)—occurs during shift-on-the-fly engagement
| - Clutch relay.
- Shift motor.
- Transfer case.
| - CHECK the 4WD engagement system. REPAIR or INSTALL as necessary. REFER to Section 308-07B.
|
- Clicking, popping or grinding—occurs while vehicle is turning
| - Inadequate or contaminated lubrication in the CV joints.
| - CHECK the CV joint boots and joints for wear or damage. REPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 205-04.
|
| - Another component contacting the halfshaft.
| - CHECK the halfshafts and the area around the halfshafts. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| | - INSPECT the front brakes for wear or damage. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 206-03.
|
| | - INSPECT the drag link, inner and outer tie-rods or idler arm for wear or damage. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 211-00.
|
| | - INSPECT the upper and lower ball joints for wear or damage. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 204-01 for front ball joints or Section 204-02 for rear ball joints.
|
| - Damaged or worn wheel bearings.
| - CHECK for abnormal wheel bearing play or roughness. REFER to Wheel Bearing Check in this section. ADJUST or INSTALL new wheel bearings as necessary. REFER to Section 204-01 for front wheel bearings or Section 204-02 for rear wheel bearings.
|
- Clicking or snapping—occurs when accelerating around a corner
| - Damaged or worn outboard CV joint.
| - INSPECT the outboard CV joint and boot. REPAIR or INSTALL a new CV joint as necessary. REFER to Section 205-04.
|
- High pitched chattering—noise from the rear axle when the vehicle is turning
| - Incorrect or contaminated lubricant.
| - CHECK the vehicle by driving in tight circles (5 clockwise, 5 counterclockwise). FLUSH and REFILL with the specified rear axle lubricant and friction modifier as necessary.
|
| - Damaged or worn differential (differential side gears and pinion gears).
| - DISASSEMBLE the differential assembly. INSPECT the differential case, pin and gears for wear or damage. REPAIR or INSTALL a new differential as necessary. REFER to Section 205-02.
|
- Buzz—buzzing noise is the same at cruise or coast/deceleration
| | - CHECK for abnormal tire wear or damage. INSTALL a new tire as necessary. REFER to Section 204-04.
|
| - Incorrect driveline angles.
| - CHECK for correct driveline angles. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 205-00.
|
- Rumble or boom—noise occurs at coast/deceleration, usually driveshaft speed related and noticeable over a wide range of speeds
| - Driveshaft is out-of-balance.
| - CHECK the driveshaft for damage, missing balance weights or undercoating. Using the VA, CHECK the driveshaft balance. CARRY OUT a driveline vibration test. REFER to Section 205-00. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| - U-joints binding or seized.
| - ROTATE the driveshaft and CHECK for rough operation or seized U-joints. INSTALL new U-joints as necessary. REFER to Section 205-01.
|
| - Excessive pinion flange runout.
| - CARRY OUT a runout check. REPAIR as necessary.
|
- Grunting—normally associated with a shudder experienced during acceleration from a dead stop
| - Driveshaft CV joint binding.
| - CLEAN the CV joint and INSTALL a new driveshaft as necessary. REFER to Section 205-01.
|
| - Loose rear axle mount bolts or suspension fasteners
| - INSPECT the rear suspension and axle. TIGHTEN the fasteners to specification.
|
- Howl—can occur at various speeds and driving conditions—affected by acceleration and deceleration
| - Incorrect ring and pinion contact, incorrect bearing preload or gear damage.
| - CHECK the ring and pinion and bearings for damage. INSPECT the ring and pinion wear pattern. REFER to Checking Tooth Contact Pattern and Condition of the Ring and Pinion component test in this section. ADJUST or INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 205-02.
|
- Chuckle—heard at coast/deceleration—also described as a knock
| - Incorrect ring and pinion contact or by damaged teeth on the coast side of the ring and pinion.
| - CHECK the ring and pinion for damage. INSPECT the ring and pinion wear pattern. REFER to Checking Tooth Contact Pattern and Condition of the Ring and Pinion component test in this section. ADJUST or INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 205-02.
|
- Knock—noise occurs at various speeds—not affected by acceleration or deceleration
| - Gear tooth damage to the drive side of the ring and pinion.
| - CHECK the differential case and ring and pinion for damage. INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 205-02.
|
| - Excessive axle shaft end play (vehicles with integral axles).
| - CHECK the axle end play using a dial indicator. INSTALL a new axle shaft or side gears as necessary. REFER to Section 205-02.
|
- Scraping noise—a continuous low pitched noise starting at low speeds
| - Worn or damaged pinion bearings.
| - CHECK the pinion bearings. INSTALL new pinion bearings as necessary. REFER to Section 205-02.
|
- Driveline shudder—occurs during acceleration from a slow speed or stop
| - Rear drive axle assembly mispositioned.
| - CHECK the axle mounts and the rear suspension for damage or wear. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| | - INSPECT the bolts. TIGHTEN the bolt nuts to specification.
|
| - Incorrect or high CV joint operating angle.
| - CHECK vehicle ride height is within limits. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| - Damaged or worn front suspension components.
| - CHECK for a loose stabilizer bar, damaged or loose strut/strut bushings or loose or worn ball joints. INSPECT the steering linkage for wear or damage. REPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 204-00.
|
| - Driveline angles out of specification.
| - CHECK for correct driveline angles. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 205-00.
|
| - U-joints binding or seized.
| - ROTATE the driveshaft and CHECK for rough operation or seized U-joints. INSTALL new U-joints as necessary. REFER to Section 205-01.
|
| - Binding the driveshaft CV joint.
| - INSPECT the driveshaft shaft CV joint and coupling shaft for a worn, or damaged condition. INSTALL a new or driveshaft assembly as necessary. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 205-01. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| | - INSPECT the bolts. TIGHTEN the bolts to specification.
|
- Driveline vibration—occurs at cruising speeds
| | - CHECK for wear or incorrect seating. INSTALL new driveshaft as necessary. REFER to Section 205-01.
|
| - Worn or damaged driveshaft center bearing support.
| - CHECK the insulator for damage or wear. ROTATE the driveshaft and CHECK for rough operation. INSTALL a new center bearing support as necessary. REFER to Section 205-01.
|
| - Loose axle pinion flange bolts.
| - INSPECT the axle pinion flange. TIGHTEN the pinion flange bolts to specification. REFER to Section 205-01.
|
| - Excessive axle pinion flange runout.
| - CARRY OUT a Runout Check. REFER to Section 205-01. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| - Driveshaft is out-of-balance.
| - CHECK the driveshaft for damage, missing balance weights or undercoating. CHECK driveshaft balance. CARRY OUT a driveline vibration test. REFER to Section 205-01. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| - Binding or damaged driveshaft CV joint.
| - INSPECT the driveshaft CV joint for wear or damage. INSTALL a new driveshaft assembly as necessary. REFER to Section 205-01. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| | - CARRY OUT a runout check. REFER to Section 205-01. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| - Incorrect lateral and radial tire/wheel runout.
| - INSPECT the tire and wheels. MEASURE tire runouts. REPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 204-04.
|
| - Driveline angles out of specification.
| - CHECK for correct driveline angles. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 205-00.
|
| - Incorrectly seated CV joint in the front wheel hub.
| - CHECK the outer CV joint for correct seating into the hub. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 205-04 for front CV joints or Section 205-05 for rear CV joints.
|
Symptom Chart — Engine Noise/Vibration
| Condition | Possible Sources | Action |
|---|
- Grinding noise—occurs during engine cranking
| - Incorrect starter motor mounting.
| - INSPECT the starter motor for correct mounting. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 303-06.
|
| | - CHECK the starter motor. REPAIR or INSTALL a new starter motor as necessary. REFER to Section 303-06.
|
| - Incorrect starter motor drive engagement.
| - INSPECT the starter motor drive and flexplate/flywheel for wear or damage. If necessary, INSTALL a new starter motor drive. REFER to Section 303-06. If necessary, INSTALL a new flexplate/flywheel. REFER to Section 303-01A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-01B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
| - Fuel injector.
- Fuel line.
- Oil pump.
- Valve lifter.
- Belt tensioner.
- Water pump.
- Obstruction of cooling fan.
| |
- Engine drumming noise—normally accompanied by vibration
| | |
| - Damaged or misaligned exhaust system.
| - INSPECT the exhaust system for loose or broken clamps and brackets, flex coupling or damper (2.0L Zetec). CARRY OUT Exhaust System Neutralizing in this section.
|
- Whistling noise—normally accompanied with poor idle condition
| | - CHECK the air intake ducts, air cleaner, throttle body and vacuum hoses for leaks and correct fit. REPAIR or ADJUST as necessary. REFER to Section 303-12.
|
| - Water pump has excessive end play or imbalance.
| - CHECK the water pump for excessive end play. INSPECT the water pump with the drive belt off for imbalance. INSTALL a new water pump as necessary. REFER to Section 303-03.
|
| - Generator has excessive end play.
| - CHECK the generator for excessive end play. REPAIR or INSTALL a new generator. REFER to Section 414-02.
|
| | - INSPECT the exhaust system for leaks. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| | - VERIFY with customer the type of gasoline used. CORRECT as necessary.
|
| | - CHECK the knock sensor. INSTALL a new knock sensor as necessary. REFER to Section 303-14.
|
| | - CHECK the spark timing. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| - High operating temperature.
| - INSPECT cooling system for leaks. CHECK the coolant level. REFILL as necessary. CHECK the coolant for the correct mix ratio. DRAIN and REFILL as needed. CHECK engine operating temperature is within specifications. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| | - CHECK the spark plugs. REPAIR or INSTALL new spark plugs as necessary. REFER to Section 303-07A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-07B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
| | |
- Knocking noise—light knocking noise, also described as piston slap—noise is most noticeable when engine is cold with light to medium acceleration—noise disappears as engine warms
| - Excessive clearance between the piston and the cylinder wall.
| - Engine cold and at high idle. Using an EngineEAR, pull a spark plug or fuel injector connector until the noise goes away. CARRY OUT a cylinder bore clearance to piston check. INSTALL a new piston. REFER to Section 303-01A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-01B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
- Knocking noise—light double knock or sharp rap sound—occurs mostly with warm engine at idle or low speeds in DRIVE—increases in relation to engine load—associated with poor lubrication history
| - Excessive clearance between the piston and the piston pin.
| |
- Knocking noise—light knocking noise is most noticeable when engine is warm—noise tends to decrease when vehicle is coasting or in neutral
| - Excessive clearance between the connecting rod bearings and the crankshaft.
| - Engine warm and at idle. Using an EngineEAR, PULL a spark plug or fuel injector connector until the noise goes away. INSTALL new bearings. REFER to Section 303-01A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-01B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
- Knocking—deep knocking noise—noise is most noticeable when engine is warm, at lower rpm and under a light load and then at float
| - Worn or damaged crankshaft main bearings.
| - CARRY OUT DERU test. CHECK for noise with vehicle at operating temperature, during medium to heavy acceleration. CHECK at idle with injector disconnected, noise does not change. INSTALL new main bearings. REFER to Section 303-01A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-01B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
- Knocking noise—occurs mostly with warm engine at light/medium acceleration
| | - CHECK the spark plug for damage or wear. INSTALL new spark plugs as necessary. REFER to Section 303-07A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-07B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
| - Carbon accumulation in combustion chamber.
| - REMOVE carbon from combustion chamber.
|
| | - CHECK the air cleaner and ducts for correct fit. INSPECT the air intake system for leaks or damage. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 303-12.
|
| - Generator electrical field or bearings.
| - CARRY OUT generator load test. REPAIR or INSTALL a new generator as necessary. REFER to Section 412-02.
|
| | |
| | - CHECK for noise with vehicle at constant speeds. CYCLE the compressor on and off and listen for a change in pitch. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 412-03.
|
| | |
- Sputter type noise—noise worse when cold, lessens or disappears when vehicle is at operating temperature
| - Damaged or worn exhaust system components.
| - INSPECT the exhaust system for leaks or damage. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 309-00.
|
- Rattling noise—noise from the upper engine (valve train)—worse when engine is cold
| | - CHECK oil level. FILL as necessary.
|
| | - INSPECT the oil for contamination. If oil is contaminated, CHECK for the source. REPAIR as necessary. CHANGE the oil and filter.
|
| | - CARRY OUT an oil pressure test. If not within specifications, REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 303-00.
|
| - Worn rocker arms/fulcrums or followers.
| - CARRY OUT a valve train analysis. INSTALL new valve train components as necessary. REFER to Section 303-01A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-01B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
| | - CARRY OUT a valve train analysis. INSTALL new valve guides as necessary. REFER to Section 303-01A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-01B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
| - Excessive runout of valve seats on the valve face.
| - CARRY OUT a valve seat runout test. INSPECT the valve face and seat. INSTALL new valves as necessary. REFER to Section 303-01A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-01B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
- Rattling noise—from the bottom of the vehicle
| - Loose muffler shields or catalytic converter shields.
| - CHECK the exhaust system for loose shields. REPAIR as necessary.
|
- Thumping noise—from the bottom of the vehicle, worse at acceleration
| - Exhaust pipe/muffler grounded to chassis.
| - CHECK the exhaust system to chassis clearance. CHECK the exhaust system hangers for damage. REPAIR as necessary.
|
- Whoosh—occurs during light vehicle acceleration—heard inside the vehicle
| - Throttling late, creating turbulence transmitted through the plastic manifold.
| - CHECK for leaks or missing seal in the dash panel.
|
- Engine vibration—increases intensity as engine rpm is increased
| | - CARRY OUT Neutral Engine Run-up (NERU) Test. ROTATE the torque converter, 120° for 3 bolt and 180° for 4 bolt. INSPECT the torque converter pilot outer diameter to crankshaft pilot inner diameter.
|
- Engine vibration—is felt with increases and decreases in engine rpm
| - Strain on exhaust mounts.
| - CARRY OUT the Exhaust System Neutralizing procedure in this section. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| - Damaged or worn powertrain/drivetrain mounts.
| - CHECK the powertrain/drivetrain mounts for damage. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| - Engine or transmission grounded to chassis.
| - INSPECT the powertrain/drivetrain for correct clearances. REPAIR as necessary.
|
- Engine vibration—vibration felt at all times
| - Excessive engine pulley runout.
| - CARRY OUT Engine Accessory Test. INSTALL a new engine pulley as necessary. REFER to Section 303-01A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-01B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
| - Damaged or worn accessory component.
| - CARRY OUT Engine Accessory Test. REPAIR or INSTALL a new component as necessary. REFER to Section 303-01A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-01B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
- Accelerator pedal vibration—felt through the pedal as a buzz
| - Throttle cable loose or misrouted.
| - INSPECT the throttle cable. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 310-02.
|
- Engine vibration—mostly at coast/neutral coast—condition improves with vehicle accelerating
| | - CHECK the ignition system. INSTALL new components as necessary.
|
- Engine vibration or shudder—occurs with light to medium acceleration above 56 km/h (35 mph)
| - Worn or damaged spark plugs.
| - INSPECT the spark plugs for cracks, high resistance or broken insulator. INSTALL a new spark plug(s) as necessary. REFER to Section 303-07A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-07B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
| | |
| | - INSPECT the spark plug wires for damage. INSTALL a new spark plug wire(s) as necessary. REFER to Section 303-07A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-07B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
| | - INSPECT the fuel for contamination. DRAIN the fuel system and refill.
|
| - Worn or damaged torque converter.
| - CHECK the torque converter. INSTALL a new torque converter as necessary. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
Symptom Chart—Idle Noise/Vibration
| Condition | Possible Sources | Action |
|---|
- Idle air control (IAC) valve moan — occurs on throttle tip-out
| - IAC valve is contaminated with oil.
| - GO to Component Tests in this section.
|
- Accessory drive belt chirp — occurs at idle or high idle, cold or hot—most common occurrence is during humid weather
| - Accessory drive belt worn, or pulley is misaligned or loose.
| - INSPECT for loose or misaligned pulleys. CHECK the drive belt for wear or damage. INSTALL new pulley(s) or accessory drive belt, as necessary. REFER to Section 303-05.
|
- Accessory drive bearing hoot — occurs at idle or high idle in cold temperatures of approximately +4°C (+40°F) or colder at first start of the day
| - Accessory drive idler or tensioner pulley bearing is experiencing stick/slip between ball bearings and bearing race.
| |
- Power steering moan — occurs at high idle and possibly at idle during the first cold start of the day in temperatures of approximately -18°C (0°F) or colder—noise can even be a severe screech for less than one minute in very cold temperatures of approximately -29°C (-20°F) or colder
| - High fluid viscosity, or plugged reservoir screen in power steering reservoir starves pump causing cavitation.
| |
- Generator whine — during high electrical loads at idle or high idle, a high pitch whine or moan is emitted from the generator
| - Generator electrical field noise.
| - Using an EngineEAR, PROBE near the generator housing. LISTEN for changes in the noise level while changing electrical loads (such as rear defrost, headlamps etc.). CARRY OUT a generator load test. REFER to Section 414-00. If the system passes the load test, the noise is from the generator bearings, INSTALL new bearings. If the system fails the load test, INSTALL a new generator. REFER to Section 414-02.
|
- Drumming noise — occurs inside the vehicle during idle or high idle, hot or cold—very low-frequency drumming is very rpm dependent
| - Exhaust system vibration excites the body resonances inducing interior noise.
- Engine vibration excites the body resonances inducing interior noise.
| |
- Hissing noise — occurs during idle or high idle that is apparent with the hood open
| - Vacuum leak or idle air control (IAC) valve flow noise.
| - USE the Ultrasonic Leak Detector/EngineEAR to LOCATE the source. SCAN the air intake system from the inlet to each cylinder intake port. DISCARD the leaking parts, and INSTALL a new component.
|
| - Vehicles with a plastic intake manifold.
| - Acceptable condition. Some plastic manifolds exhibit this noise, which is the effect of the plastic manifold.
|
- Automatic transmission buzz or hiss
| - Incorrect driveline angles.
| - CHECK for correct driveline angles. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 205-00.
|
| - Worn or damaged main control solenoids or valves.
| - Using a transmission tester, ACTIVATE the solenoids to duplicate sound. INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
- Manual Transmission Clutch throw-out bearing whine—a change in noise pitch or loudness while depressing the clutch pedal
| | |
- Heating, vacuum and air conditioning (HVAC) system chirp — most audible inside the vehicle—listen for a change in noise pitch or loudness while changing the HVAC system blower speed
| - Damaged or worn HVAC blower bearing.
| |
- Air conditioning (A/C) clutch ticking — occurs when the compressor clutch engages
| - Acceptable noise.
- Incorrect air gap.
| - LISTEN to the clutch to determine if the noise occurs with clutch engagement. A small amount of noise is acceptable. If the noise is excessive, CHECK the A/C clutch air gap. INSPECT the A/C clutch for wear or damage. INSTALL a new clutch as necessary. REFER to Section 412-03.
|
- Intermittent rattle, or scraping/rubbing noise
| - Loose exhaust heat shield(s).
| - INSPECT the exhaust system for loose parts using a glove or clamps to verify cause. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 309-00.
|
| - Wiring, hose or other part interfering with the accessory drive belt or pulley.
| - INSPECT the accessory drive system closely verifying there is adequate clearance to all rotating components. REPAIR as necessary.
|
- Engine ticking or knocking noise — occurs during idle or high idle during the first cold start of the day
| - Piston noise or valvetrain noise (bled down lifter/lash adjuster).
| |
- A continuous, speed-dependent rattle from the engine — occurs during idle or high idle during the first cold start of the day and disappears as the engine warms up
| - Piston noise or valvetrain noise (bled down lifter/lash adjuster).
| |
- Idle vibration—a low-frequency vibration (5-20 Hz) or mild shake that is felt through the seat/floorpan
| | - Using the diagnostic tool, CHECK the ignition system. CARRY OUT a cylinder power test. REFER to Section 303-00.
|
| - Engine or torque converter out of balance.
| - VERIFY the torque converter to crankshaft pilot clearance is correct, REPAIR as necessary. RE-INDEX the torque converter on the flex plate by 120° on a 3-bolt converter or 180° for a 4-bolt converter. REFER to Section 307-01. RETEST the vehicle.
|
- Idle vibration—a high-frequency vibration (20–80 Hz) or buzz, that is felt through the steering wheel or seat
| - Exhaust system mounts bound up.
| - VERIFY concern occurs at engine firing frequency. CHECK that the exhaust system vibrates at the same frequency as the engine. ADD 9–14 km (20–30 lb.) to the tail pipe to test, CARRY OUT Exhaust System Neutralizing in this section.
|
| - Power steering lines grounded out.
| - INSPECT that the power steering lines are not contacting the chassis or each other. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| | |
Symptom Chart—Squeak and Rattle
| Condition | Possible Sources | Action |
|---|
- Squeak—heard inside the vehicle when closing/opening the door
| - Insufficient lubrication on the door hinge or check strap.
| - LUBRICATE the hinge or check strap.
|
| - Internal door components loose, rubbing or misaligned.
| - CHECK the inside of the door. TIGHTEN or ALIGN as necessary. USE the Rotunda Squeak and Rattle Kit to ISOLATE any rubbing components.
|
- Squeak—heard inside the vehicle when closing/opening the window
| - Worn or damaged glass run/channel.
| |
- Squeak—heard outside of vehicle when closing/opening the door
| - Exhaust shield rubbing against the chassis or exhaust pipe.
| - CHECK the exhaust system. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 309-00.
|
- Squeak—occurs with initial brake pedal application
| | - Under certain conditions, asbestos free pads can generate a squeak noise. This noise is normal and does not indicate a concern.
|
- Squeak—a constant noise that occurs with brake pedal applications
| - Damaged or worn disc brake pads.
| - INSPECT the pads for oil, grease or brake fluid contamination. CHECK for glazed linings. A brake disc with hard spots will also cause a squeak type noise. REPAIR or INSTALL new brake pads as necessary. REFER to Section 206-03.
|
- Squeak—noise occurs over bumps or when turning
| - Worn control arm bushings.
| - INSPECT the control arm bushings. Spray with lubricant and CARRY OUT a "bounce test" to determine which bushing. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 204-01 for front bushings or Section 204-02 for rear bushings.
|
| - Worn or damaged shock absorber/strut.
| - INSPECT the shock absorber for damage. CARRY OUT a "bounce test" to isolate the noise. INSTALL a new shock absorber/strut as necessary. REFER to Section 204-01 for front shock absorber/strut or Section 204-02 for rear shock absorber/strut.
|
- Rattle—heard when closing/opening the door or window
| - Loose internal door mechanism, bracket or attachment.
| - REPEAT the motion or CARRY OUT a "tap test" to duplicate the noise. INSPECT the door for loose components. TIGHTEN loose components or USE the Rotunda Squeak and Rattle Kit to ISOLATE any rattling components.
|
- Squeak or rattle—heard inside the vehicle over rough roads/bumps
| - Misaligned glove compartment door/hinge.
| - ALIGN the glove compartment door.
|
| - Instrument panel trim loose or misaligned.
| - INSPECT the instrument panel trim for missing or loose clips or screws. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| - Loose interior component or trim.
| - CARRY OUT a "touch test". ELIMINATE the noise by pressing or pulling on interior trim and components. USE the Rotunda Squeak and Rattle Kit to ISOLATE any rattling/squeaking components.
|
- Squeak or rattle—noise with a vibration concern
| - Damaged or worn sub-frame mounts.
| - INSPECT the upper and lower absorbers for damage or wear. CHECK the sub-frame for damage. CHECK the nuts and bolts are tightened to specifications. TIGHTEN as necessary.
|
Symptom Chart—Steering Noise/Vibration
| Condition | Possible Sources | Action |
|---|
- Steering grunt or shudder — occurs when turning into or out of a turn at low speeds (temperature sensitive)
| - Steering gear or power steering hoses.
| - GO to Steering Gear Grunt/Shudder Test component test in this section.
|
- Steering System clonk—hydraulic knocking sound
| - Air in the steering hydraulic system.
| - CHECK for leaks in the system. PURGE the air from the system. REFER to Section 211-00.
|
- Power steering pump moan — loud humming noise occurs when the steering wheel is rotated to the stop position. Produces a 120-600 Hz frequency that changes with rpm
| - Power steering hose grounded out to chassis.
| - INSPECT the power steering hoses. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| | - CHECK for leaks in the system. PURGE the air from the system. REFER to Section 211-00.
|
| | - INSPECT the isolators for wear or damage. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| | - CHECK the fluid level. REFILL as necessary.
|
| - Power steering pump brackets loose or misaligned.
| - CHECK bolts, brackets and bracket alignment. TIGHTEN bolts to specification. REPAIR or INSTALL new brackets as necessary. REFER to Section 211-02.
|
- Steering gear clunk — occurs only while cornering over a bump (can be temperature sensitive)
| | - INSPECT the steering gear for loose mounting bolts. TIGHTEN as necessary. REFER to Section 211-02.
|
- Feedback (rattle, chuckle or knocking noise in the steering gear) — a condition where roughness is felt in the steering wheel when the vehicle is driven over rough surfaces
| - Column intermediate/flexible shaft joints damaged or worn.
| |
| - Loose, damaged or worn tie-rod ends.
| - TIGHTEN the nuts to specification or INSTALL new tie-rod ends as necessary. REFER to Section 211-03.
|
| - Steering gear insulators or mounting bolts loose or damaged.
| - TIGHTEN the bolts or INSTALL new bolts as necessary. REFER to Section 211-02.
|
| - Steering column intermediate shaft bolts are loose.
| - TIGHTEN the bolts to specification.
|
| - Steering column damaged or worn.
| - REPAIR or INSTALL a new steering column as necessary. REFER to Section 211-04.
|
| - Loose suspension bushings, bolts or ball joints.
| - INSPECT the suspension system. TIGHTEN or INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 204-01 for front suspension or Section 204-02 for rear suspension.
|
- Feedback (nibble at the steering wheel) — a condition where slight rotational movement is felt in the steering wheel when the vehicle is driven over rough or grooved surfaces
| - Lateral runout in the tire or wheel.
| |
| - Yoke spring in the steering gear.
| - CHECK TSBs for revised yoke spring for applicable vehicles.
|
- Accessory drive belt squeal/chirp—when rotating the steering wheel from stop to stop
| - Loose or worn accessory drive belt.
| - ADJUST or INSTALL a new accessory belt as necessary. REFER to Section 303-05.
|
| - Steering column intermediate/flexible shaft-to-steering gear is binding or misaligned.
| - REPAIR or INSTALL a new intermediate/flexible shaft as necessary. REFER to Section 211-04.
|
| - Grounded or loose steering column boot at the dash panel.
| |
| - Damaged or worn steering gear input shaft and valve.
| - REPAIR or INSTALL a new steering gear as necessary. REFER to Section 211-02.
|
| - Loose bolts or attaching brackets.
| - TIGHTEN the bolts to specifications.
|
| - Loose, worn or insufficiently lubricated column bearings.
| - LUBRICATE or INSTALL new steering column bearings as necessary. REFER to Section 211-04.
|
| - Steering shaft insulators damaged or worn.
| |
| - Intermediate/flexible shaft compressed or extended.
| - INSPECT the rubber spider coupling for damage. INSTALL a new intermediate/flexible shaft. REFER to Section 211-04.
|
- Steering column squeak or cracks
| - Insufficiently lubricated steering shaft bushings.
| - LUBRICATE the steering shaft and shaft tube seals.
|
| - Loose or misaligned steering column shrouds.
| - TIGHTEN or ALIGN the steering column shrouds.
|
| - Steering wheel rubbing against steering column shrouds.
| - REPOSITION the steering column shrouds.
|
| - Insufficient lubricated speed control slip ring.
| - LUBRICATE the speed control slip ring.
|
| - Upper or lower bearing sleeve out of position.
| - REPOSITION the bearing sleeves.
|
- Power steering pump noisy
| - Incorrect assembly of components.
- Imperfections on the outside diameter or end surface of the power steering pump rotor.
- Damaged or worn power steering pump rotor splines.
- A crack on the inner surface of the power steering pump cam.
- Interference between the power steering pump rotor and cam.
- Damaged or worn power steering pump rotor and pressure plates.
| - REPAIR or INSTALL a new power steering pump as necessary. REFER to Section 211-02.
|
- Power steering pump swish noise
| - Power steering fluid flow into the bypass valve of the pump valve housing with fluid temperature below 54°C (130°F).
| |
- Power steering pump whine noise
| | - PURGE the air from the system. REFER to Section 211-00. CHECK for a leak in the system.
|
| - Damaged power steering pump cam.
| - REPAIR or INSTALL a new power steering pump as necessary. REFER to Section 211-02.
|
| - Damaged valve cover O-ring seal.
| - REPAIR or INSTALL a new power steering pump as necessary. REFER to Section 211-02.
|
- Power steering pump clicking (mechanical) noise
| - Power steering pump rotor slippers too long, excessive rotor slipper-to-slot clearance or damaged or worn rotor assembly.
| - REPAIR or INSTALL a new power steering pump as necessary. REFER to Section 211-02.
|
- Power steering pump clatter noise
| - Damaged corners on the outside diameter or the power steering rotor or distorted rotor slipper ring.
| - REPAIR or INSTALL a new power steering pump as necessary. REFER to Section 211-02.
|
Symptom Chart—Suspension Noise/Vibration
| Condition | Possible Sources | Action |
|---|
- Squeak or grunt—noise from the front suspension, occurs more in cold ambient temperatures—more noticeable over rough roads or when turning
| - Front stabilizer bar insulators.
| - Under these conditions, the noise is acceptable. CHECK TSBs.
|
- Clunk—noise from the front suspension, occurs in and out of turns
| - Loose front struts or shocks.
| - INSPECT for loose nuts or bolts. TIGHTEN to specifications. REFER to Section 204-01.
|
- Clunk—noise from the rear suspension, occurs when shifting from reverse to drive
| - Loose rear suspension components.
| - INSPECT for loose or damaged rear suspension components. REPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 204-02.
|
- Click or pop—noise from the front suspension—more noticeable over rough roads or over bumps
| - Worn or damaged ball joints.
| - CARRY OUT a ball joint inspection. INSTALL new control arm as necessary. REFER to Section 204-01.
|
- Click or pop (FWD vehicles)—noise occurs when vehicle is turning
| - Worn or damaged ball joints.
| - CARRY OUT a ball joint inspection. INSTALL new control arm as necessary. REFER to Section 204-01.
|
- Click or snap (FWD vehicles)—occurs when accelerating around a corner
| - Damaged or worn outboard CV joint.
| - INSPECT the outboard CV joint and boot. REPAIR or INSTALL a new CV joint as necessary. REFER to Section 205-04.
|
- Front suspension noise—a squeak, creak or rattle noise—occurs mostly over bumps or rough roads
| - Steering components.
- Loose or bent front struts or shock absorbers.
- Damaged spring or spring mounts.
- Damaged or worn control/radius arm bushings.
- Worn or damaged stabilizer bar bushings or links.
| |
- Rear suspension noise—a squeak, creak or rattle noise—occurs mostly over bumps or rough roads
| - Loose or bent rear shock absorbers.
- Damaged spring or spring mounts.
- Damaged or worn control arm bushings.
| |
- Shudder—occurs during acceleration from a slow speed or stop
| - Rear drive axle assembly mispositioned.
| - CHECK the axle mounts and the rear suspension for damage or wear. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| - Incorrect or high CV joint operating angle.
| - CHECK vehicle ride height is within limits. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| - Damaged or worn front suspension components.
| - CHECK for a loose stabilizer bar, damaged or loose strut/strut bushings or loose or worn ball joints. INSPECT the steering linkage for wear or damage. REPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary.
|
- Shimmy—most noticeable on coast/deceleration—also hard steering condition
| - Excessive positive caster.
| - CHECK the caster alignment angle. CORRECT as necessary. REFER to Section 204-00.
|
Symptom Chart—Tire Noise/Vibration
| Condition | Possible Sources | Action |
|---|
- Tire noise—hum/moan at constant speeds
| | - SPIN the tire and CHECK for tire wear. INSTALL a new tire as necessary. INSPECT for damaged/worn suspension components. CARRY OUT wheel alignment.
|
- Tire noise—noise tone lowers as the vehicle speed is lowered
| | - BALANCE the tire and road test. INSTALL a new tire as necessary. REFER to Section 204-04.
|
- Tire noise — ticking noise, changes with speed
| - Nail puncture or stone in tire tread.
| - INSPECT the tire. REPAIR as necessary.
|
- Wheel and tire—vibration and noise concern is directly related to vehicle speed and is not affected by acceleration, coasting or decelerating
| | |
- Tire wobble or shudder — occurs at lower speeds
| | - SPIN the tire and CHECK for abnormal wheel bearing play or roughness. ADJUST or INSTALL new wheel bearings as necessary. REFER to Section 204-01 for front bearings or Section 204-02 for rear bearings.
|
| | - INSPECT the wheel for damage. INSTALL a new wheel as necessary. REFER to Section 204-04.
|
| - Damaged or worn suspension components.
| - INSPECT the suspension components for wear or damage. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| | - CHECK the wheel nuts. TIGHTEN to specification. REFER to Section 204-04.
|
| - Damaged or uneven tire wear.
| - SPIN the tire and CHECK for abnormal tire wear or damage. INSTALL a new tire as necessary. REFER to Section 204-04.
|
- Tire shimmy or shake— occurs at lower speeds
| - Wheel/tire out of balance.
| - BALANCE the wheel/tire assembly.
|
| | - CHECK for abnormal tire wear. INSTALL a new tire as necessary. REFER to Section 204-04.
|
| - Excessive radial runout of wheel or tire.
| - CARRY OUT a radial runout test of the wheel and tire. INSTALL a new tire as necessary. REFER to Section 204-04.
|
| - Worn or damaged wheel studs or elongated stud holes.
| - INSPECT the wheel studs and wheels. INSTALL new components as necessary.
|
| - Excessive lateral runout of the wheel or tire.
| - CARRY OUT a lateral runout test of the wheel and tire. CHECK the wheel, tire and hub. REPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary.
|
| - Foreign material between the brake disc and hub or in the brake disc fins.
| - CLEAN the mounting surfaces of the brake disc and hub. CHECK the brake disc fins for material.
|
- High speed shake or shimmy—occurs at high speeds
| - Excessive wheel hub runout.
- Damaged or worn tires.
- Damaged or worn wheel bearings.
- Worn or damaged suspension or steering linkage components.
- Brake disc or drum imbalance.
| |
Symptom Chart—Transmission (Manual) and Transfer Case Noise/Vibration
| Condition | Possible Sources | Action |
|---|
- Clutch rattling noise—occurs with clutch engaged, noise changes/disappears with clutch pedal depressed
| - Flywheel bolts, clutch housing bolts or clutch pressure plate bolts loose.
| - TIGHTEN the bolts to specifications. CHECK the bolts for damage.
|
- Clutch squeaking noise—noise is heard when the clutch is operated—vehicle moves slowly or creeps when the clutch is disengaged—can also be difficult to shift into first and reverse gear
| - Pilot bearing seized or damaged.
| |
- Clutch squeaking noise—occurs with clutch pedal depressed/released
| - Worn clutch pedal shaft or bushings.
| - INSPECT the clutch pedal for wear or damage. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 308-02.
|
- Clutch whirring/rattle noise—occurs when clutch pedal is depressed
| - Worn, damaged or misaligned clutch release bearing.
| |
- Clutch grating/grinding noise—occurs when clutch pedal is depressed
| - Clutch pressure plate fingers bent or worn.
| - INSPECT the clutch pressure plate release fingers. INSTALL a new pressure plate as necessary. REFER to Section 308-01.
|
| - Contact surface of clutch release bearing worn or damaged.
| |
- Clutch chatter—a small amount of noise when clutch pedal is released at initial take-off
| | - Acceptable operating condition.
|
- Clutch chatter/grabs—in some cases a shudder is felt—occurs with clutch pedal depressed/released
| - Damaged or worn powertrain/driveline mounts.
| - INSPECT the powertrain/drivetrain mounts. INSTALL new mounts as necessary. REFER to Section 308-03.
|
| - Binding or dragging plunger of the clutch master cylinder or slave cylinder.
| - CHECK the master and slave cylinder operation. INSPECT the components for damage or wear. INSTALL a new master or slave cylinder as necessary. REFER to Section 308-02.
|
| - Grease or oil on the clutch disc facing.
| - CHECK the input shaft seal and rear main oil seal. REPAIR as necessary. INSTALL a new clutch disc. REFER to Section 308-03.
|
| - Clutch disc surface glazed or damaged.
| - INSPECT the clutch disc surface for a glazed, hardened or damage condition. CARRY OUT a disc check. INSTALL a new clutch disc as necessary. REFER to Section 308-01.
|
| - Damaged or worn clutch pressure plate.
| - INSPECT the clutch pressure plate for wear or damage. INSTALL a new clutch pressure plate as necessary. REFER to Section 308-01.
|
| - Flywheel surface damaged or glazed.
| - INSPECT the flywheel for damage or wear. CARRY OUT a flexplate/flywheel runout check. INSTALL a new flywheel as necessary. REFER to Section 303-01A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-01B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
- Clutch chatter noise—noise when clutch pedal is released at initial take-off—clutch is hard to engage and disengage
| - Pilot bearing worn, damaged or not correctly aligned in bore.
| - INSPECT the clutch pressure plate release fingers for uneven wear, clutch components burnt or a seized pilot bearing. INSTALL a new pilot bearing as necessary. REFER to Section 308-01.
|
| - Loose flywheel bolts.
- Damaged or loose clutch pressure plate.
- Excessive flywheel runout.
| |
- Transmission rattling/clattering noise—noise at idle or on light acceleration from a stop—gear selection difficult
| - Gearshift lever joint worn or damaged.
| |
| | |
| - Gearshift linkage rods worn or damaged.
| - CHECK the linkage bushings for wear. INSTALL new linkage rods as necessary. REFER to Section 308-06.
|
- Transmission rattling/clattering noise—occurs in neutral or in gear, at idle
| - Incorrect fluid level or fluid quality.
| - CHECK that the transmission is filled to the correct level and with the specified fluid. REFER to Section 308-03.
|
- Transmission rattling/clattering noise—noise at idle in neutral
| - Worn or rough reverse idler gear.
| - CHECK the reverse idler gear. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 308-03.
|
| - Rough running engine, cylinder misfire.
| - CHECK the ignition system. CARRY OUT a cylinder power test. REFER to Section 303-00.
|
| - Excessive backlash in gears
| - CHECK the gear backlash. ADJUST as necessary. REFER to Section 308-03.
|
| | |
- Transmission whine—a mild whine at extreme speeds or high rpm
| - Rotating gears/geartrain.
| |
- Transmission whine—a high pitched whine, also described as a squeal
| - Transmission gears are worn (high mileage vehicle).
| - Result of normal gear wear. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 308-03.
|
| | - INSPECT the gear sets for an uneven wear pattern on the face of the gear teeth. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 308-03.
|
| - Damaged or worn transmission bearing.
| - INSPECT the transmission bearings. INSTALL new bearings as necessary. REFER to Section 308-03.
|
- Transmission growling/humming—noise occurs in the forward gears—the noise is more prominent when the gear is loaded—the problem gear can be located as the noise occurs in a specific gear position
| - Gear is cracked, chipped or rough.
| - INSPECT the transmission gears for damage or wear. INSTALL new gears as necessary. REFER to Section 308-03.
|
- Transmission hissing—noise in neutral or in forward gears—as bearings wear or break up, the noise changes to a thumping noise
| - Damaged or worn bearings.
| - INSPECT the transmission bearings. INSTALL new bearings as necessary. REFER to Section 308-03.
|
- Transmission knocking/thudding—noise at low speeds in forward gears
| - Bearings with damaged balls or rollers or with pitted and spalled races.
| - INSPECT the transmission bearings. INSTALL new bearings as necessary. REFER to Section 308-03.
|
- Transmission rumble/growl—noise at higher speeds in forward gears, more pronounced in a coast/deceleration condition
| - Incorrect driveline angle.
| - CHECK the driveline angle. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 205-00.
|
| - Driveshaft out of balance or damaged.
| - CHECK the driveshaft for damage, missing balance weights or undercoating. Using the EVA, CHECK the driveshaft balance. CARRY OUT a driveline vibration test. REFER to Section 205-01. REPAIR as necessary.
|
- Transmission rumble/growl—noise at all speeds in forward gears, more pronounced in a heavy acceleration condition
| - Damaged or worn transmission bearing or gears (high mileage vehicles).
| - CHECK transmission fluid for excessive metal particles. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 308-03.
|
- Transfer case whine—noise at all ranges
| - Incorrect fluid level or fluid quality.
| - CHECK that the transfer case is filled to the correct level and with the specified fluid. REFER to Section 308-07B.
|
| - Under-inflated or oversized tires.
| - CONFIRM that the tires and wheels are correct for the vehicle. CHECK that the tire inflation pressures are correct. REFER to Section 204-04.
|
- Transfer case growl/rumble—noise
| - Damaged or worn bearings or gears.
| |
- Transfer case vibration—vibration felt with vehicle in 4WD
| - Transfer case mounting.
- Driveshaft out of balance.
- Excessive flange runout.
| |
Symptom Chart—Transmission (Automatic) Noise/Vibration
| Condition | Possible Sources | Action |
|---|
- Rattle—occurs at idle or at light acceleration from a stop
| - Damaged engine or transmission mounts.
| - CHECK the powertrain/drivetrain mounts for damage. INSTALL new mounts as necessary. REFER to Section 303-01A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-01B for 3.0L (4V) engine.
|
| - A loose front exhaust pipe heat shield.
| - REPAIR or INSTALL a new heat shield as necessary.
|
| - Loose inspection plate or dust cover plate.
| - CHECK for loose bolts. TIGHTEN to specifications. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
| - Loose flex plate to converter nuts.
| - CHECK for loose nuts. TIGHTEN to specifications. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
- Whine—pitch increases with vehicle speed—starts in first and second gear, decreases or goes away at higher gears
| - Damaged or worn low one-way clutch.
- Damaged or worn intermediate one-way clutch.
- Friction elements.
- Damaged or worn planetary or sun gear.
| - INSPECT the transmission for wear or damage. REPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
- Whine—the pitch changes with engine speed
| - A worn or damaged accessory drive component.
| - CARRY OUT the Engine Accessory Test. REPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 303-05.
|
| | - CHECK that the transmission is filled to the correct level. ADD fluid as necessary. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
| - Partially blocked filter.
| - INSPECT the filter. CLEAN or INSTALL a new filter as necessary.
|
| - Worn or damaged torque converter.
| - CARRY OUT the torque converter service and replacement check. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
| - Worn or damaged front pump.
| - INSPECT the front pump. INSTALL a new front pump as necessary. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
- Whine—pitch changes with vehicle speed
| | - REPAIR or INSTALL new gears as necessary.
|
- Whine/moan type noise—pitch increases or changes with vehicle speed
| - Damaged engine or transmission mount.
| |
| - U-joints worn or damaged.
| - INSPECT the U-joints for wear or damage. INSTALL new U-joints as necessary. REFER to Section 205-01.
|
| - Damaged or worn differential ring and pinion.
| - INSPECT the differential ring and pinion for damage. CARRY OUT the Checking Tooth Contact Pattern and Condition of the Ring and Pinion component test in this section. REPAIR or INSTALL a new differential ring and pinion as necessary. REFER to Section 205-02.
|
| - Planetary gears nicked or chipped.
| - CHECK the planetary gears for damage. INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
- Whistle—noise is high pitched, constant—changes in pitch with throttle position
| - Hydraulic pressure in the main control.
| - INSPECT the main control. REPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
| - Incorrect band/clutch apply pressure.
| - CARRY OUT the line pressure tests. REPAIR or INSTALL components as necessary. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
| - Worn or damaged torque converter.
| - CARRY OUT the torque converter service and replacement check. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
- Clunk—occurs when shifting from PARK to a drive or reverse position
| - Damaged powertrain mounts.
| - INSPECT the powertrain mounts for damage. INSTALL new mounts as necessary. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
| - Damaged or worn pinion bearings.
| - CHECK for abnormal bearing play or roughness. INSTALL new bearings as necessary. REFER to Section 205-02.
|
| - Worn driveshaft CV joint.
| - INSPECT the CV joint. INSTALL a new driveshaft as necessary. REFER to Section 205-01.
|
| - Worn friction elements or excessive clutch pack end plate play.
| - INSPECT the transmission for wear. CHECK that all end play and clearances are within specification. REPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
- Bump—occurs when shifting from PARK to a drive or reverse position—similar to Clunk but with no sound
| | |
| - Incorrect driveline angles.
| - CHECK for correct driveline angles. REPAIR as necessary. REFER to Section 205-00.
|
| - Worn or damaged main control solenoids or valves.
| - Using a transmission tester, ACTIVATE the solenoids to duplicate sound. INSTALL new components as necessary. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
- Vibration—a high frequency (20–80 Hz) that is felt through the seat or gear shifter—changes with engine speed
| - Transmission cooler lines grounded out.
| - CHECK the transmission cooler lines. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| - Flexplate to torque converter nuts loose.
| - CHECK the flexplate nuts. TIGHTEN to specification. REFER to Section 307-01.
|
| - Fluid filler tube grounded out.
| - CHECK the fluid filler tube. REPAIR as necessary.
|
| - Shift cable incorrectly routed, grounded out or loose.
| - CHECK the shift cable. REPAIR as necessary.
|
- Shutter or chatter—occurs with light to medium acceleration from low speeds or a stop
| - Electrical inputs/outputs.
- Vehicle wiring harness.
- Incorrect inputs/outputs from the powertrain control module (PCM), digital transmission range (TR) sensor, brake pedal position (BPP) sensor, throttle position (TP) sensor, transmission speed sensor (TSS), output speed shaft (OSS) sensor or the torque converter clutch (TCC).
| - CARRY OUT a Torque Converter Clutch Operation Test. RUN on-board diagnostics or self–test. CLEAR the DTCs, ROAD TEST and RERUN on-board diagnostics or self–test.
|
Pinpoint Tests
The pinpoint tests are a step-by-step diagnostic process designed to determine the cause of a condition. It may not always be necessary to follow a pinpoint test to its conclusion. Carry out only the steps necessary to correct the condition. Then, test the system for normal operation. Sometimes, it is necessary to remove various vehicle components to gain access to the component requiring testing. For additional information, refer to the appropriate section for removal and installation procedures. Reinstall all components after verifying system operation is normal.
PINPOINT TEST A: BRAKE VIBRATION/SHUDDER
| CONDITIONS | DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS |
|---|
| A1 ROAD TEST THE VEHICLE—LIGHT BRAKING |
|  Check that the wheel and tires are correct for the vehicle. Inspect the tires for abnormal wear patterns. |
|  Road test the vehicle. Warm the brakes by slowing the vehicle a few times from 80–32 km/h (50 to 20 mph) using light braking applications. At highway speeds of 89–97 km/h (55-60 mph), apply the brake using a light pedal force. |
|
- Is there a vibration/shudder felt in the steering wheel, seat or brake pedal?
 Yes Yes
 No No |
| A2 ROAD TEST THE VEHICLE—MODERATE TO HEAVY BRAKING |
|  Road test the vehicle. At highway speeds of 89–97 km/h (55-60 mph), apply the brake using a moderate to heavy pedal force. |
|
- Is there a vibration/shudder?
 Yes YesFor vehicles with ABS, GO to A3. For vehicles with standard brakes, GO to A4.
 No NoVehicle is OK. VERIFY condition with customer. TEST the vehicle for normal operation. |
| A3 NORMAL ACTUATION OF THE ABS SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS |
|  During moderate to heavy braking, noise from the hydraulic control unit (HCU) and pulsation in the brake pedal can be observed. Pedal pulsation coupled with noise during heavy braking or on loose gravel, bumps, wet or snowy surfaces is acceptable and indicates correct functioning of the ABS system. Pedal pulsation or steering wheel nibble whose frequency is proportioned to the vehicle speed indicates a concern with a brake or suspension component. |
|
- Is the vibration/shudder vehicle speed sensitive?
 Yes Yes
 No NoThe brake system is operating correctly. |
| A4 APPLICATION OF THE PARKING BRAKE |
|  NOTE: NOTE: Begin at the front of the vehicle unless the vibration or shudder has been isolated to the rear. This test is not applicable to vehicles with drum-in-hat type parking brakes. For vehicles with drum-in-hat parking brakes, proceed to the next test. For all other vehicles, apply the parking brake to identify if the problem is in the front or rear brake. At highway speeds of 89–97 km/h (55-60 mph), lightly apply the parking brake until the vehicle slows down. Release the parking brake immediately after the test. |
|
- Is there a vibration/shudder?
 Yes Yes
 No No |
| A5 CHECK THE FRONT WHEEL BEARINGS |
| |
|
- Are the wheel bearings OK?
 Yes Yes
 No NoINSPECT the wheel bearings. ADJUST or REPAIR as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation. |
| A6 CHECK THE FRONT SUSPENSION |
|  Check the front suspension for: - broken or loose bolts
- damaged springs
- worn or damaged lower control arm bushings
- loose or rough front bearings
- uneven tire wear
|
|
- Are all the suspension components in satisfactory condition?
 Yes Yes
 No NoREPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation. |
| A7 RESURFACE THE FRONT BRAKE DISCS |
|   CAUTION: Do not use a bench lathe to machine brake discs. CAUTION: Do not use a bench lathe to machine brake discs.NOTE: Follow the manufacturer's instructions to machine the brake discs. After machining, make sure the brake disc meets the thickness specification. Refer to Brake Disc Machining in this section. Resurface the front brake discs. Road test the vehicle. |
|
- Is the vibration/shudder present?
 Yes Yes
 No NoVehicle is OK. |
| A8 CHECK THE REAR SUSPENSION |
|  Check the rear suspension for: - broken or loose bolts
- damaged or worn springs or spring bushings
- worn or damaged upper and lower control arm bushings
- worn or damaged trailing arms
- loose or rough rear bearings
- uneven tire wear
|
|
- Are all the suspension components in satisfactory condition?
 Yes Yes
 No NoREPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation. |
| A9 RESURFACE THE REAR BRAKE DISC OR DRUM |
|   CAUTION: Do not use a bench lathe to machine brake discs. CAUTION: Do not use a bench lathe to machine brake discs.NOTE: Follow the manufacturers instructions to machine the brake discs. After machining, make sure the brake disc meets the thickness specification. Refer to Brake Disc Machining in this section. Resurface the rear brake disc or drums. Road test the vehicle. |
|
- Is the vibration/shudder present?
 Yes YesCHECK the front suspension for wear or damage, RESURFACE the front brake discs. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No NoVehicle is OK. |
PINPOINT TEST B: ENGINE TICKING NOISE
| CONDITIONS | DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS |
|---|
| B1 CHECK FOR TICKING NOISE AT THE FUEL RAIL |
|  Disconnect the first fuel line clip. |
|
- Is the ticking noise gone?
 Yes YesCHECK for TSB for applicable vehicle. REPAIR as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| B2 CHECK FOR TICKING NOISE AT THE FUEL INJECTOR |
|  Using an EngineEAR, listen at the fuel injectors by placing a probe on each injector. To isolate the faulty injector, disconnect the injector electrical connector and listen for the noise. |
|
- Is the fuel injector the source of the ticking noise?
 Yes YesINSTALL a new fuel injector. REFER to Section 303-04A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-04B for 3.0L (4V) engine. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| B3 CHECK THE BELT TENSIONER FOR TICKING NOISE |
|  Inspect the front engine accessory drive (FEAD). Check for the belt tensioner bottoming at end of travel or not at end of stroke. |
|  Using an EngineEAR, listen at the belt tensioner. |
|
- Is the belt tensioner the source of the noise?
 Yes YesINSTALL a new belt tensioner. REFER to Section 303-05. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| B4 CHECK THE WATER PUMP FOR TICKING NOISE |
|  Using an EngineEAR, listen at the water pump for ticking noise. |
|
- Is the water pump the source of the noise?
 Yes YesINSTALL a new water pump. REFER to Section 303-03. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| B5 CHECK FOR AN OBSTRUCTION OF THE COOLING FAN |
|  Inspect the cooling fan for obstructions. |
|  Check the cooling fan and shroud for wear or damage. |
|
- Was there an obstruction or does the cooling fan show signs of damage?
 Yes YesREPAIR or INSTALL a new cooling fan. REFER to Section 303-03. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| B6 CHECK THE OIL PUMP FOR TICKING NOISE |
|  Check the oil pump using EngineEARs and probe at the oil filter adapter to verify the oil pump as a source. |
|
- Is the oil pump the source of the noise?
 Yes Yes
 No No |
| B7 CHECK VALVE LIFTERS OR LASH ADJUSTERS FOR CORRECT OPERATION |
|  Check valve lifter/lash adjuster for correct operation, using EngineEARs. |
|
- Are the valve lifters/lash adjusters operating correctly?
 Yes YesVERIFY customer concern. CONDUCT a diagnosis of other suspect components.
 No NoINSTALL a new valve lifter/lash adjuster(s). TEST the system for normal operation. |
PINPOINT TEST C: FRONT ENGINE ACCESSORY DRIVE BEARING HOOT
| CONDITIONS | DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS |
|---|
| C1 CHECK THE ACCESSORY DRIVE IDLER AND TENSIONER PULLEY BEARINGS |
|  Carry out the Vehicle Cold Soak Procedure in this section. |
| |
|  Place an EngineEAR probe directly on the pulley center post or bolt to verify which bearing is making the noise. |
| |
|
- Is either bearing making the noise?
 Yes YesINSTALL a new pulley/idler. REFER to Section 303-05. CARRY OUT the Vehicle Cold Soak Procedure and TEST the system for normal operation.
 No NoCONDUCT a diagnosis on other suspect accessory drive components. |
PINPOINT TEST D: POWER STEERING MOAN
| CONDITIONS | DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS |
|---|
| D1 CHECK THE POWER STEERING SYSTEM |
|  Carry out the Vehicle Cold Soak Procedure in this section. |
| |
|  Turn the steering wheel while the noise is occurring and listen for changes in sound pitch or loudness. |
| |
|
- Does the sound pitch or loudness change while turning the steering wheel?
 Yes Yes
 No NoCONDUCT a diagnosis on other suspect accessory drive components. |
| D2 VERIFY THE SOURCE |
| |
|  Place an EngineEAR probe near the power steering pump/reservoir while the noise is occurring. While an assistant turns the steering wheel, listen for changes in sound pitch or loudness. |
| |
|
- Does the sound pitch or loudness change while turning the steering wheel?
 Yes YesVERIFY that the supply tube to the pump is unobstructed. CHECK the fluid condition and level. DRAIN the fluid and REFILL. CARRY OUT the Vehicle Cold Soak Procedure and TEST the system for normal operation. REFER to Section 211-02.
 No NoNormal system operation. |
PINPOINT TEST E: DRUMMING NOISE
| CONDITIONS | DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS |
|---|
| E1 CHECK THE EXHAUST SYSTEM |
| |
|  Increase the engine rpm until the noise is the loudest. Note the engine rpm. |
| |
|  Add approximately 9 kg (20 lb) of weight to the exhaust system. Place the weight at the tailpipe and test. |
| |
|  Increase the engine rpm and listen for the drumming noise. Note the engine rpm if the noise occurs. |
| |
| 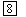 Using a vibration analyzer, determine the amount of vibration that occurs with the drumming noise. |
|
- Is the noise/vibration reduced or eliminated, or does the noise/vibration occur at a different rpm?
 Yes Yes
 No No |
| E2 POWERTRAIN/DRIVETRAIN MOUNT NEUTRALIZING |
| |
|
- Is the noise reduced or eliminated?
 Yes YesVehicle is OK. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No NoCONDUCT diagnosis of other suspect components. |
PINPOINT TEST F: ENGINE TICKING, KNOCKING OR CONTINUOUS RATTLE
| CONDITIONS | DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS |
|---|
| F1 CHECK FOR NOISE AT THE VALVE COVERS AND THE FRONT COVERS (OHC ENGINES) |
|  Carry out the Vehicle Cold Soak Procedure in this section. |
| |
|  NOTE: NOTE: For a short-duration ticking noise, multiple engine starts may be necessary. Using an EngineEAR, listen closely at the valve covers and the front covers by placing the probe near the surface of the valve cover and then on the surface front cover. |
| |
|
- Is the noise source apparent?
 Yes YesREMOVE the appropriate cover and INSPECT for loose, worn/broken components. REPAIR as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| F2 CHECK FOR NOISE AT THE CYLINDER BLOCK |
| |
|  Using an EngineEAR, listen closely at the cylinder block by placing a probe on or near each freeze plug. |
| |
|
- Is the noise source apparent?
 Yes YesREPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary.
 No No |
| F3 CHECK FOR NOISE WHILE DISCONNECTING EACH FUEL INJECTOR ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR, ONE AT A TIME |
| |
|  Disconnect each fuel injector electrical connector, one at a time, to decrease piston force and listen for the noise. |
| |
|
- Is the noise reduced or eliminated?
 Yes YesINSTALL a new fuel injector. REFER to Section 303-04A for 2.0L Zetec engine or Section 303-04B for 3.0L (4V) engine. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No NoINSPECT accessory drive or the transmission as a possible source. |
PINPOINT TEST G: FRONT SUSPENSION NOISE
| CONDITIONS | DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS |
|---|
| G1 ROAD TEST THE VEHICLE |
|  Test drive the vehicle. |
|  During the road test, drive the vehicle over a rough road. Using ChassisEARs, determine from which area/component the noise is originating. |
|
- Is there a squeak, creak or rattle noise?
 Yes Yes
 No NoThe suspension system is OK. CONDUCT a diagnosis on other suspect systems. |
| G2 INSPECT THE STEERING SYSTEM |
|  Raise and support the vehicle. For additional information, refer to Section 100-02. |
|  Check the steering system for wear or damage. Carry out a steering linkage test. |
|  Inspect the tire wear pattern. Refer to Tire Wear Patterns chart in this section. |
|
- Are the steering components worn or damaged?
 Yes YesREPAIR the steering system. INSTALL new components as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| G3 FRONT SHOCK ABSORBER/STRUT CHECK |
|  Check the front shock absorbers/strut mounts for loose bolts or nuts. |
|  Check the front shock absorbers/struts for damage. Carry out a shock absorber check. |
|
- Are the front shock absorbers/struts loose or damaged?
 Yes YesTIGHTEN to specifications if loose. INSTALL new front shock absorbers/struts if damaged. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| G4 CHECK THE FRONT SPRINGS |
|  Check the front spring and front spring mounts/brackets for wear or damage. |
|
- Are the front springs or spring mounts/brackets worn or damaged?
 Yes YesREPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| G5 CHECK THE CONTROL ARMS/RADIUS ARMS |
|  Inspect the control arm bushings for wear or damage. |
|  Inspect for twisted or bent control arm/radius arm. |
|
- Are the control arm/radius arms damaged or worn?
 Yes YesREPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| G6 CHECK THE STABILIZER BAR/TRACK BAR |
|  Check the stabilizer bar/track bar bushings and links for damage or wear. |
|  Check the stabilizer bar/track bar for damage. |
|  Check for loose or damaged stabilizer bar/track bar isolators or brackets. |
|
- Are the stabilizer bar/track bar components loose, worn or damaged?
 Yes YesREPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No NoSuspension system is OK. CONDUCT diagnosis on other suspect systems. |
PINPOINT TEST H: REAR SUSPENSION NOISE
| CONDITIONS | DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS |
|---|
| H1 ROAD TEST THE VEHICLE |
|  Test drive the vehicle. |
|  During the road test, drive the vehicle over a rough road. Using ChassisEARs, determine from which area/component the noise is originating. |
|
- Is there a squeak, creak or rattle noise?
 Yes Yes
 No NoThe suspension system is OK. Conduct a diagnosis on other suspect systems. |
| H2 REAR SHOCK ABSORBER/STRUT CHECK |
| |
|  Check the rear shock absorber/strut mounts for loose bolts or nuts. |
|  Check the rear shock absorbers/struts for damage. Carry out a shock absorber check. |
|
- Are the rear shock absorbers/struts loose or damaged?
 Yes YesTIGHTEN to specifications if loose. INSTALL new rear shock absorbers/struts if damaged. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| H3 CHECK THE REAR SPRINGS |
|  Check the rear springs and rear spring mounts/brackets for wear or damage. |
|
- Are the rear springs or spring mounts/brackets worn or damaged?
 Yes YesREPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| H4 CHECK THE CONTROL ARMS/TRAILING ARMS |
|  Inspect the control arm/trailing arm bushings for wear or damage. Check for loose control arm/trailing arm bolts. |
|  Inspect for twisted or bent control arms/trailing arms. |
|
- Are the control arms/trailing arms loose, damaged or worn?
 Yes YesREPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No NoSuspension system is OK. CONDUCT diagnosis on other suspect systems. |
PINPOINT TEST I: WHEEL AND TIRE
PINPOINT TEST J: HIGH SPEED SHAKE OR SHIMMY
| CONDITIONS | DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS |
|---|
| J1 CHECK FOR FRONT WHEEL BEARING ROUGHNESS |
|  Chock the rear wheels. |
|  Raise and support the front end of the vehicle so that the front wheel and tire assemblies can spin. Refer to Section 100-02. |
|  Spin the front tires by hand. |
|
- Do the wheel bearings feel rough?
 Yes YesINSPECT the wheel bearings. REPAIR as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| J2 CHECK THE END PLAY OF THE FRONT WHEEL BEARINGS |
|  Check the end play of the front wheel bearings. |
|
 Yes Yes
 No NoADJUST or REPAIR as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation. |
| J3 MEASURE THE LATERAL RUNOUT AND THE RADIAL RUNOUT OF THE FRONT WHEELS ON THE VEHICLE |
|  Measure the lateral runout and the radial runout of the front wheels on the vehicle. Go to Pinpoint Test I. |
|
- Are the measurements within specifications?
 Yes Yes
 No NoINSTALL new wheels as necessary and BALANCE the assembly. TEST the system for normal operation. |
| J4 MEASURE THE LATERAL RUNOUT OF THE FRONT TIRES ON THE VEHICLE |
|  Measure the lateral runout of the front tires on the vehicle. Go to Pinpoint Test I. |
|
- Is the runout within specifications?
 Yes Yes
 No NoINSTALL new tires as necessary and BALANCE the assembly. TEST the system for normal operation. |
| J5 MEASURE THE RADIAL RUNOUT OF THE FRONT TIRES ON THE VEHICLE |
|  Measure the radial runout of the front tires on the vehicle. Go to Pinpoint Test I. |
|
- Is the runout within specifications?
 Yes YesBALANCE the front wheel and tire assemblies. If any tire cannot be balanced, INSTALL a new tire. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| J6 MATCH MOUNT THE TIRE AND WHEEL ASSEMBLY |
|  Mark the high runout location on the tire and also on the wheel. Break the assembly down and rotate the tire 180 degrees (halfway around) on the wheel. Inflate the tire and measure the radial runout. |
|
- Is the runout within specifications?
 Yes YesBALANCE the assembly. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No NoIf the high spot is not within 101.6 mm (4 inches) of the first high spot on the tire, GO to J7. |
| J7 MEASURE THE WHEEL FLANGE RUNOUT |
|  Dismount the tire and mount the wheel on a wheel balancer. Measure the runout on both wheel flanges. Go to Pinpoint Test I. |
|
- Is the runout within specifications?
 Yes YesLOCATE and MARK the low spot on the wheel. INSTALL the tire, matching the high spot on the tire with the low spot on the wheel. BALANCE the assembly. TEST the system for normal operation. If the condition persists,GO to J8.
 No NoINSTALL a new wheel. CHECK the runout on the new wheel. If the new wheel is within limits, LOCATE and MARK the low spot. INSTALL the tire, matching the high spot on the tire with the low spot on the wheel. BALANCE the assembly. TEST the system for normal operation. If the condition persists, GO to J8. |
| J8 CHECK FOR VIBRATION FROM THE FRONT OF THE VEHICLE |
 WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (34 mph) using the speedometer reading, since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Exceeding a speed of 55 km/h (34 mph) or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported can result in tire disintegration or differential failure, which can cause serious personal injury and extensive vehicle damage. WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (34 mph) using the speedometer reading, since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Exceeding a speed of 55 km/h (34 mph) or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported can result in tire disintegration or differential failure, which can cause serious personal injury and extensive vehicle damage. |
|  Spin the front wheel and tire assemblies with a wheel balancer while the vehicle is raised on a hoist. Feel for vibration in the front fender or while seated in the vehicle. |
|
- Is the vibration present?
 Yes YesSUBSTITUTE known good wheel and tire assemblies as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No NoFor front wheel drive vehicles, check the driveline components. TEST the system for normal operation. For rear wheel drive vehicles, GO to J9. |
| J9 CHECK FOR VIBRATION FROM THE REAR OF THE VEHICLE |
 WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (34 mph) using the speedometer reading, since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Exceeding a speed of 55 km/h (34 mph) or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported can result in tire disintegration or differential failure, which can cause serious personal injury and extensive vehicle damage. WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (34 mph) using the speedometer reading, since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Exceeding a speed of 55 km/h (34 mph) or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported can result in tire disintegration or differential failure, which can cause serious personal injury and extensive vehicle damage. |
|  Chock the front wheels. |
|  Raise and support the rear end of the vehicle so that the rear wheel and tire assemblies can spin. Refer to Section 100-02. |
|  Engage the drivetrain and carefully accelerate the drive wheels while checking for vibration. |
|
- Is the vibration present?
 Yes Yes
 No NoTEST the system for normal operation. |
| J10 CHECK THE DRIVETRAIN |
 WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (34 mph) using the speedometer reading, since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Exceeding a speed of 55 km/h (34 mph) or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported can result in tire disintegration or differential failure, which can cause serious personal injury and extensive vehicle damage. WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (34 mph) using the speedometer reading, since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Exceeding a speed of 55 km/h (34 mph) or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported can result in tire disintegration or differential failure, which can cause serious personal injury and extensive vehicle damage. |
| |
|  Secure the brake drums (if so equipped), by installing wheel hub bolt nuts, reversed. |
|  Carefully accelerate the drivetrain while checking for vibration. |
|
- Is the vibration present?
 Yes YesCHECK/TEST the drivetrain and driveline components. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No NoSUBSTITUTE known good wheel and tire assemblies as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation. |
PINPOINT TEST K: CLUTCH VIBRATION
| CONDITIONS | DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS |
|---|
| K1 CHECK ENGINE COMPONENTS FOR GROUNDING |
|  NOTE: NOTE: Make sure the clutch is the cause of the vibration concern. The vibration should occur during clutch operation. The clutch can also be difficult to engage or disengage. Eliminate all related systems before checking the clutch components. NOTE: Check the driveline angles and driveshaft runout before disassembling the clutch system. Refer to Section 205-00 for the correct driveline angle specifications. Check the powertrain/drivetrain mounts, exhaust manifolds or other engine components for grounding on the chassis. |
|
- Are any mounts or engine components grounded?
 Yes YesREPAIR as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| K2 CHECK THE ACCESSORY DRIVE BELT |
|  Remove the accessory drive belt. |
|
- Does the vibration stop with the accessory drive belt removed?
 Yes YesDIAGNOSE the accessory drive components.
 No No |
| K3 CHECK FOR LOOSE CLUTCH PRESSURE PLATE BOLTS |
|  Check for loose clutch pressure plate bolts. Inspect the clutch pressure plate for damage or for material between the pressure plate and flywheel. |
|
- Are there any loose bolts or damage?
 Yes YesTIGHTEN the bolts to specifications or if damaged, INSTALL a new clutch pressure plate. REFER to Section 308-01. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| K4 CHECK THE CLUTCH DISC SPRINGS |
|  Check for worn, broken or loose clutch disc springs. |
|
- Are the clutch springs worn, broken or loose?
 Yes YesINSTALL a new clutch disc. REFER to Section 308-01. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| K5 CHECK THE CLUTCH DISC SPLINES |
|  Inspect the clutch disc splines for damage or wear. |
|
 Yes YesINSTALL a new clutch disc. REFER to Section 308-01. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| K6 CHECK THE FLYWHEEL BOLTS |
|  Check for loose flywheel bolts. |
|
 Yes YesTIGHTEN the bolts to specifications. REFER to Section 308-01. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| K7 CHECK THE FLYWHEEL SURFACE |
|  Inspect the flywheel surface for wear or damage. Check the flywheel runout. |
|
- Is there any damage or excessive wear?
 Yes Yes
 No NoClutch system is normal. CONDUCT a diagnosis on other suspect systems. |
PINPOINT TEST L: TRANSFER CASE VIBRATION
| CONDITIONS | DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS |
|---|
| L1 INSPECT THE TRANSFER CASE |
|  Inspect the transfer case for loose or missing mounting bolts. Check for fluid seepage between the transfer case and the transmission. |
|
- Are the mounting bolts missing or loose?
 Yes YesTIGHTEN to specifications or INSTALL new bolts as necessary. REFER to Section 308-07B. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| L2 INSPECT THE REAR DRIVESHAFT |
|  NOTE: NOTE: Verify that the driveshaft and pinion flange index marks are aligned. Inspect the driveshaft for missing weights, damage or undercoating. |
|  Inspect the U-joints for freedom of movement. |
|  Inspect the constant velocity joint for freedom of movement. |
|  Check driveshaft runout and, if necessary, check the pinion flange runout. |
|
- Are the driveshaft or U-joints worn or damaged or misaligned?
 Yes YesINSTALL a new driveshaft as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| L3 CHECK THE DRIVELINE ANGLES |
|  Measure the rear driveshaft and pinion angles. Refer to Section 205-00. |
|  Measure the front driveshaft and pinion angles. Refer to Section 205-00. |
|
- Are the driveline angles incorrect?
 Yes YesREPAIR as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| L4 ROAD TEST WITH THE REAR DRIVESHAFT REMOVED |
|  NOTE: NOTE: Index mark the driveshaft to the pinion flange and to the output shaft before removal. Remove the rear driveshaft. |
|  Test drive the vehicle. |
|
 Yes YesINSTALL and BALANCE the rear driveshaft. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No No |
| L5 TRANSFER CASE OUTPUT FLANGE INSPECTION |
|  Inspect the output flange for damage. |
|  Inspect the driveshaft constant velocity joints for wear or damage. |
|
- Are the splines worn or damaged?
 Yes YesREPAIR or INSTALL new components as necessary. TEST the system for normal operation.
 No NoThe transfer case is OK. CONDUCT a diagnosis on other suspect systems. |
Component Tests
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
- Open the hood.
NOTE: Key symptom is elevated idle speed while noise is occurring.
NOTE: "Snapping" the throttle can induce the noise.
Verify the condition by operating the vehicle for a short time.
- Inspect the IAC. If physical evidence of contamination exists, install a new IAC.
- While the noise is occurring, either place an EngineEAR probe near the IAC valve and the inlet tube, or create a 6.35 mm (0.25 in)-12.7 mm (0.50 in) air gap between the inlet tube and the clean air tube. If the IAC valve is making the noise, install a new IAC valve.
- Test the vehicle for normal operation.
Steering Gear Grunt/Shudder Test
- Start and run the vehicle to operating temperature.
- Set engine idle speed to 1,200 rpm.
 CAUTION: Do not hold the steering wheel against the stops for more than three to five seconds at a time. Damage to the power steering pump will occur.
CAUTION: Do not hold the steering wheel against the stops for more than three to five seconds at a time. Damage to the power steering pump will occur.
Rotate the steering wheel to the RH stop, then turn the steering wheel 90 degrees back from that position. Turn the steering wheel slowly in a 15 to 30 degree arc.
- Turn the steering wheel another 90 degrees. Turn the steering wheel slowly in a 15 to 30 degree arc.
- Repeat the test with power steering fluid at different temperatures.
- If a light grunt is heard or a low (50-200 Hz) shudder is present, this is a normal steering system condition.
- If a loud grunt is heard or a strong shudder is felt, fill and purge the power steering system.
Checking Tooth Contact Pattern and Condition of the Ring and Pinion
There are two basic types of conditions that will produce ring and pinion noise. The first type is a howl or chuckle produced by broken, cracked, chipped, scored or forcibly damaged gear teeth and is usually quite audible over the entire speed range. The second type of ring and pinion noise pertains to the mesh pattern of the gear pattern. This gear noise can be recognized as it produces a cycling pitch or whine. Ring and pinion noise tends to peak in a narrow speed range or ranges, and will tend to remain constant in pitch.
- Raise and support the vehicle. Refer to Section 100-02.
- Drain the axle lubricant. Refer to Section 205-02.
- Remove the carrier assembly or the axle housing cover depending on the axle type. Refer to Section 205-02.
- Inspect the gear set for scoring or damage.

- In the following steps, the movement of the contact pattern along the length is indicated as toward the" heel" or "toe" of the differential ring gear.
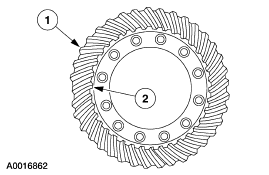
- Apply a marking compound to a third of the gear teeth on the differential ring gear. Rotate the differential ring gear several complete turns in both directions until a good, clear tooth pattern is obtained. Inspect the contact patterns on the ring gear teeth.
- A good contact pattern should be centered on the tooth. It can also be slightly toward the toe. There should always be some clearance between the contact pattern and the top of the tooth.
- Tooth contact pattern shown on the drive side of the gear teeth.
- A high, thick contact pattern that is worn more toward the toe.
- Tooth contact pattern shown on the drive side of the gear teeth.
- The high contact pattern indicates that the drive pinion is not installed deep enough into the carrier.
- The differential ring gear backlash is correct, a thinner drive pinion shim is needed. A decrease will move the drive pinion toward the differential ring gear.
- A high, thin contact pattern that is worn toward the toe.
- Tooth contact pattern shown on the drive side of the gear teeth.
- The drive pinion depth is correct. Increase the differential ring gear backlash.
- A contact pattern that is worn in the center of the differential ring gear tooth toward the heel.
- Tooth contact pattern shown on the drive side of the gear teeth.
- The low contact pattern indicates that the drive pinion is installed too deep into the carrier.
- The differential ring gear backlash is correct. A thicker drive pinion shim is needed.
- A contact pattern that is worn at the top of the differential ring gear tooth toward the heel.
- Tooth contact pattern shown on the drive side of the gear teeth.
- The pinion gear depth is correct. Decrease the differential ring gear backlash.
Tire Wear Patterns and Frequency Calculations
Tire Wear Chart
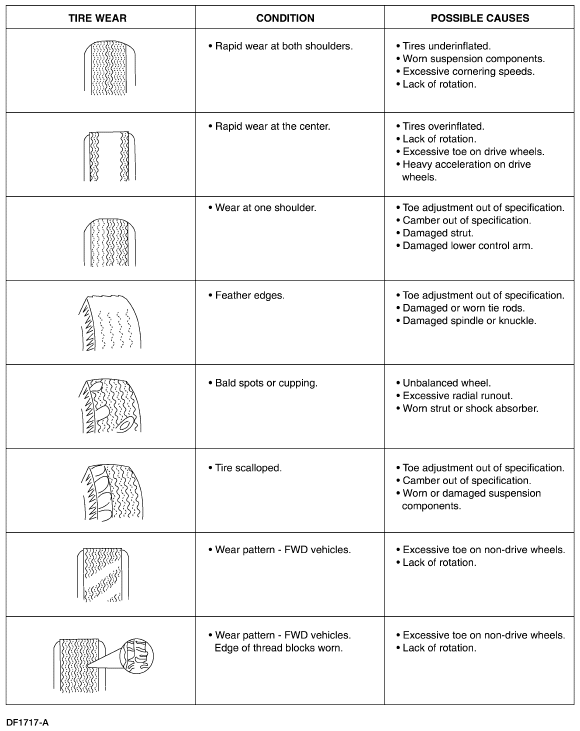
Wheel and tire NVH concerns are directly related to vehicle speed and are not generally affected by acceleration, coasting or decelerating. Also, out-of-balance wheel and tires can vibrate at more than one speed. A vibration that is affected by the engine rpm, or is eliminated by placing the transmission in NEUTRAL is not related to the tire and wheel. As a general rule, tire and wheel vibrations felt in the steering wheel are related to the front tire and wheel assemblies. Vibrations felt in the seat or floor are related to the rear tire and wheel assemblies. This can initially isolate a concern to the front or rear.
Careful attention must be paid to the tire and wheels. There are several symptoms that can be caused by damaged or worn tire and wheels. Carry out a careful visual inspection of the tires and wheel assemblies. Spin the tires slowly and watch for signs of lateral or radial runout. Refer to the tire wear chart to determine the tire wear conditions and actions.
For a vibration concern, use the vehicle speed to determine tire/wheel frequency and rpm. Calculate tire and wheel rpm and frequency by carrying out and following:
- Measure the diameter of the tire.
- Record the speed at which the vibration occurs.
- Obtain the corresponding tire and wheel rpm and frequency from the Tire Speed and Frequency Chart.
- If the vehicle speed is not listed, divide the vehicle speed at which the vibration occurs by 16 (km/h (10 mph). Multiply that number by 16 km/h (10 mph) tire rpm listed for that tire diameter in the chart. Then divide that number by 60. For example: a 40 mph vibration with 835 mm (33 in) tires. 40 ÷10 = 4. Multiply 4 by 105 = 420 rpm. Divide 420 rpm by 60 seconds = 7 Hz at 40mph.
Tire Speed and Frequency Chart
| Tire Diameter | Tire RPM/Hz | Tire RPM/Hz | Tire RPM/Hz | Tire RPM/Hz |
|---|
| mm (inch) | @ 16 km/h (10 mph) | @ 80 km/h (50 mph) | @ 97 km/h (60 mph) | @ 113 km/h (70 mph) |
| 483 (19) | 182 | 910/15 | 1092/18 | 1274/21 |
| 508 (20) | 173 | 865/14 | 1038/17 | 1211/20 |
| 533 (21) | 165 | 825/14 | 990/16 | 1155/19 |
| 560 (22) | 158 | 790/13 | 948/16 | 1106/18 |
| 585 (23) | 151 | 755/13 | 906/15 | 1057/18 |
| 610 (24) | 145 | 725/12 | 870/14 | 1015/17 |
| 635 (25) | 139 | 695/12 | 834/14 | 973/16 |
| 660 (26) | 134 | 670/11 | 804/13 | 938/16 |
| 685 (27) | 129 | 645/11 | 774/13 | 903/15 |
| 710 (28) | 124 | 620/10 | 744/12 | 868/14 |
| 735 (29) | 119 | 595/10 | 714/12 | 833/14 |
| 760 (30) | 115 | 575/10 | 690/11 | 805/13 |
| 785 (31) | 111 | 555/9 | 666/11 | 777/13 |
| 810 (32) | 108 | 540/9 | 648/11 | 756/13 |
| 835 (33) | 105 | 525/9 | 630/10 | 735/12 |
| 864 (34) | 102 | 510/8 | 612/10 | 714/12 |











 WARNING: Block the front and rear wheels, and apply the parking brake and the service brake, or injury to personnel can result.
WARNING: Block the front and rear wheels, and apply the parking brake and the service brake, or injury to personnel can result. CAUTION: Do not carry out the Engine Load Test for more than five seconds or damage to the transmission or transaxle can result.
CAUTION: Do not carry out the Engine Load Test for more than five seconds or damage to the transmission or transaxle can result. WARNING: Block the front and rear wheels, and apply the parking brake and the service brake, or injury to personnel can result.
WARNING: Block the front and rear wheels, and apply the parking brake and the service brake, or injury to personnel can result. CAUTION: Limit engine running time to one minute or less with belts removed or serious engine damage will result.
CAUTION: Limit engine running time to one minute or less with belts removed or serious engine damage will result. CAUTION: Never probe moving parts.
CAUTION: Never probe moving parts. Check that the wheel and tires are correct for the vehicle. Inspect the tires for abnormal wear patterns.
Check that the wheel and tires are correct for the vehicle. Inspect the tires for abnormal wear patterns. Road test the vehicle. Warm the brakes by slowing the vehicle a few times from 80–32 km/h (50 to 20 mph) using light braking applications. At highway speeds of 89–97 km/h (55-60 mph), apply the brake using a light pedal force.
Road test the vehicle. Warm the brakes by slowing the vehicle a few times from 80–32 km/h (50 to 20 mph) using light braking applications. At highway speeds of 89–97 km/h (55-60 mph), apply the brake using a light pedal force. Yes
Yes No
No Road test the vehicle. At highway speeds of 89–97 km/h (55-60 mph), apply the brake using a moderate to heavy pedal force.
Road test the vehicle. At highway speeds of 89–97 km/h (55-60 mph), apply the brake using a moderate to heavy pedal force. Yes
Yes No
No During moderate to heavy braking, noise from the hydraulic control unit (HCU) and pulsation in the brake pedal can be observed. Pedal pulsation coupled with noise during heavy braking or on loose gravel, bumps, wet or snowy surfaces is acceptable and indicates correct functioning of the ABS system. Pedal pulsation or steering wheel nibble whose frequency is proportioned to the vehicle speed indicates a concern with a brake or suspension component.
During moderate to heavy braking, noise from the hydraulic control unit (HCU) and pulsation in the brake pedal can be observed. Pedal pulsation coupled with noise during heavy braking or on loose gravel, bumps, wet or snowy surfaces is acceptable and indicates correct functioning of the ABS system. Pedal pulsation or steering wheel nibble whose frequency is proportioned to the vehicle speed indicates a concern with a brake or suspension component. Yes
Yes No
No NOTE: Begin at the front of the vehicle unless the vibration or shudder has been isolated to the rear.
NOTE: Begin at the front of the vehicle unless the vibration or shudder has been isolated to the rear. Yes
Yes No
No Check the front wheel bearings. Refer to Wheel Bearing Check in this section.
Check the front wheel bearings. Refer to Wheel Bearing Check in this section. Yes
Yes No
No Check the front suspension for:
Check the front suspension for: Yes
Yes No
No
 CAUTION: Do not use a bench lathe to machine brake discs.
CAUTION: Do not use a bench lathe to machine brake discs. Yes
Yes No
No Check the rear suspension for:
Check the rear suspension for: Yes
Yes No
No
 CAUTION: Do not use a bench lathe to machine brake discs.
CAUTION: Do not use a bench lathe to machine brake discs. Yes
Yes No
No Disconnect the first fuel line clip.
Disconnect the first fuel line clip. Yes
Yes No
No Using an EngineEAR, listen at the fuel injectors by placing a probe on each injector. To isolate the faulty injector, disconnect the injector electrical connector and listen for the noise.
Using an EngineEAR, listen at the fuel injectors by placing a probe on each injector. To isolate the faulty injector, disconnect the injector electrical connector and listen for the noise. Yes
Yes No
No Inspect the front engine accessory drive (FEAD). Check for the belt tensioner bottoming at end of travel or not at end of stroke.
Inspect the front engine accessory drive (FEAD). Check for the belt tensioner bottoming at end of travel or not at end of stroke. Using an EngineEAR, listen at the belt tensioner.
Using an EngineEAR, listen at the belt tensioner. Yes
Yes No
No Using an EngineEAR, listen at the water pump for ticking noise.
Using an EngineEAR, listen at the water pump for ticking noise. Yes
Yes No
No Inspect the cooling fan for obstructions.
Inspect the cooling fan for obstructions. Check the cooling fan and shroud for wear or damage.
Check the cooling fan and shroud for wear or damage. Yes
Yes No
No Check the oil pump using EngineEARs and probe at the oil filter adapter to verify the oil pump as a source.
Check the oil pump using EngineEARs and probe at the oil filter adapter to verify the oil pump as a source. Yes
Yes No
No Check valve lifter/lash adjuster for correct operation, using EngineEARs.
Check valve lifter/lash adjuster for correct operation, using EngineEARs. Yes
Yes No
No Carry out the Vehicle Cold Soak Procedure in this section.
Carry out the Vehicle Cold Soak Procedure in this section.
 Place an EngineEAR probe directly on the pulley center post or bolt to verify which bearing is making the noise.
Place an EngineEAR probe directly on the pulley center post or bolt to verify which bearing is making the noise.

 Yes
Yes No
No Carry out the Vehicle Cold Soak Procedure in this section.
Carry out the Vehicle Cold Soak Procedure in this section.

 Turn the steering wheel while the noise is occurring and listen for changes in sound pitch or loudness.
Turn the steering wheel while the noise is occurring and listen for changes in sound pitch or loudness.

 Yes
Yes No
No

 Place an EngineEAR probe near the power steering pump/reservoir while the noise is occurring. While an assistant turns the steering wheel, listen for changes in sound pitch or loudness.
Place an EngineEAR probe near the power steering pump/reservoir while the noise is occurring. While an assistant turns the steering wheel, listen for changes in sound pitch or loudness.

 Yes
Yes No
No

 Increase the engine rpm until the noise is the loudest. Note the engine rpm.
Increase the engine rpm until the noise is the loudest. Note the engine rpm.

 Add approximately 9 kg (20 lb) of weight to the exhaust system. Place the weight at the tailpipe and test.
Add approximately 9 kg (20 lb) of weight to the exhaust system. Place the weight at the tailpipe and test.

 Increase the engine rpm and listen for the drumming noise. Note the engine rpm if the noise occurs.
Increase the engine rpm and listen for the drumming noise. Note the engine rpm if the noise occurs.

 Using a vibration analyzer, determine the amount of vibration that occurs with the drumming noise.
Using a vibration analyzer, determine the amount of vibration that occurs with the drumming noise. Yes
Yes No
No Carry out Powertrain/Drivetrain Mount Neutralizing in this section. Test the system for normal operation.
Carry out Powertrain/Drivetrain Mount Neutralizing in this section. Test the system for normal operation. Yes
Yes No
No Carry out the Vehicle Cold Soak Procedure in this section.
Carry out the Vehicle Cold Soak Procedure in this section.

 NOTE: For a short-duration ticking noise, multiple engine starts may be necessary.
NOTE: For a short-duration ticking noise, multiple engine starts may be necessary.

 Yes
Yes No
No

 Using an EngineEAR, listen closely at the cylinder block by placing a probe on or near each freeze plug.
Using an EngineEAR, listen closely at the cylinder block by placing a probe on or near each freeze plug.

 Yes
Yes No
No

 Disconnect each fuel injector electrical connector, one at a time, to decrease piston force and listen for the noise.
Disconnect each fuel injector electrical connector, one at a time, to decrease piston force and listen for the noise.

 Yes
Yes No
No Test drive the vehicle.
Test drive the vehicle. During the road test, drive the vehicle over a rough road. Using ChassisEARs, determine from which area/component the noise is originating.
During the road test, drive the vehicle over a rough road. Using ChassisEARs, determine from which area/component the noise is originating. Yes
Yes No
No Raise and support the vehicle. For additional information, refer to Section 100-02.
Raise and support the vehicle. For additional information, refer to Section 100-02. Check the steering system for wear or damage. Carry out a steering linkage test.
Check the steering system for wear or damage. Carry out a steering linkage test. Inspect the tire wear pattern. Refer to Tire Wear Patterns chart in this section.
Inspect the tire wear pattern. Refer to Tire Wear Patterns chart in this section. Yes
Yes No
No Check the front shock absorbers/strut mounts for loose bolts or nuts.
Check the front shock absorbers/strut mounts for loose bolts or nuts. Check the front shock absorbers/struts for damage. Carry out a shock absorber check.
Check the front shock absorbers/struts for damage. Carry out a shock absorber check. Yes
Yes No
No Check the front spring and front spring mounts/brackets for wear or damage.
Check the front spring and front spring mounts/brackets for wear or damage. Yes
Yes No
No Inspect the control arm bushings for wear or damage.
Inspect the control arm bushings for wear or damage. Inspect for twisted or bent control arm/radius arm.
Inspect for twisted or bent control arm/radius arm. Yes
Yes No
No Check the stabilizer bar/track bar bushings and links for damage or wear.
Check the stabilizer bar/track bar bushings and links for damage or wear. Check the stabilizer bar/track bar for damage.
Check the stabilizer bar/track bar for damage. Check for loose or damaged stabilizer bar/track bar isolators or brackets.
Check for loose or damaged stabilizer bar/track bar isolators or brackets. Yes
Yes No
No Test drive the vehicle.
Test drive the vehicle. During the road test, drive the vehicle over a rough road. Using ChassisEARs, determine from which area/component the noise is originating.
During the road test, drive the vehicle over a rough road. Using ChassisEARs, determine from which area/component the noise is originating. Yes
Yes No
No Raise and support the vehicle. REFER to Section 100-02.
Raise and support the vehicle. REFER to Section 100-02. Check the rear shock absorber/strut mounts for loose bolts or nuts.
Check the rear shock absorber/strut mounts for loose bolts or nuts. Check the rear shock absorbers/struts for damage. Carry out a shock absorber check.
Check the rear shock absorbers/struts for damage. Carry out a shock absorber check. Yes
Yes No
No Check the rear springs and rear spring mounts/brackets for wear or damage.
Check the rear springs and rear spring mounts/brackets for wear or damage. Yes
Yes No
No Inspect the control arm/trailing arm bushings for wear or damage. Check for loose control arm/trailing arm bolts.
Inspect the control arm/trailing arm bushings for wear or damage. Check for loose control arm/trailing arm bolts. Inspect for twisted or bent control arms/trailing arms.
Inspect for twisted or bent control arms/trailing arms. Yes
Yes No
No NOTE: Wheel or tire vibrations felt in the steering wheel are most likely related to the front wheel or tire. Vibration felt through the seat are most likely related to the rear wheel or tire. This may not always be true, but it can help to isolate the problem to the front or rear of the vehicle.
NOTE: Wheel or tire vibrations felt in the steering wheel are most likely related to the front wheel or tire. Vibration felt through the seat are most likely related to the rear wheel or tire. This may not always be true, but it can help to isolate the problem to the front or rear of the vehicle. During the road test, if the vibration can be eliminated by placing the vehicle in neutral or is affected by the speed of the engine, the cause is not the wheels or tires.
During the road test, if the vibration can be eliminated by placing the vehicle in neutral or is affected by the speed of the engine, the cause is not the wheels or tires. Yes
Yes No
No Check the front wheel bearings. Refer to Wheel Bearing Check in this section.
Check the front wheel bearings. Refer to Wheel Bearing Check in this section. Yes
Yes No
No Check the tires for missing weights.
Check the tires for missing weights. Check the wheels for damage.
Check the wheels for damage. Inspect the tire wear pattern. Refer to the Tire Wear Patterns chart in this section.
Inspect the tire wear pattern. Refer to the Tire Wear Patterns chart in this section. Yes
Yes No
No
 Spin the tires slowly and watch for signs of lateral runout.
Spin the tires slowly and watch for signs of lateral runout.
 Spin the tires slowly and watch for signs of radial runout.
Spin the tires slowly and watch for signs of radial runout. Yes
Yes No
No

 Measure the radial runout of the wheel and tire assembly. A typical specification for total radial runout is 1.15mm (0.059inch).
Measure the radial runout of the wheel and tire assembly. A typical specification for total radial runout is 1.15mm (0.059inch). Yes
Yes No
No Measure the radial runout of the wheel. A typical specification for total radial runout is 1.14mm (0.045 inch).
Measure the radial runout of the wheel. A typical specification for total radial runout is 1.14mm (0.045 inch). Yes
Yes No
No Measure the pilot or bolt circle runout. A typical specification for radial runout is:
Measure the pilot or bolt circle runout. A typical specification for radial runout is: Yes
Yes No
No

 Measure the lateral runout of the wheel and tire assembly. A typical specification for total lateral runout is 2.5mm (0.098inch).
Measure the lateral runout of the wheel and tire assembly. A typical specification for total lateral runout is 2.5mm (0.098inch). Yes
Yes No
No Measure the lateral runout of the wheel. A typical specification for total radial runout is 1.2mm (0.047inch).
Measure the lateral runout of the wheel. A typical specification for total radial runout is 1.2mm (0.047inch). Yes
Yes No
No Measure the flange face lateral runout. A typical specification for lateral runout is:
Measure the flange face lateral runout. A typical specification for lateral runout is: Yes
Yes No
No Chock the rear wheels.
Chock the rear wheels. Raise and support the front end of the vehicle so that the front wheel and tire assemblies can spin. Refer to Section 100-02.
Raise and support the front end of the vehicle so that the front wheel and tire assemblies can spin. Refer to Section 100-02. Spin the front tires by hand.
Spin the front tires by hand. Yes
Yes No
No Check the end play of the front wheel bearings.
Check the end play of the front wheel bearings. Yes
Yes No
No Measure the lateral runout and the radial runout of the front wheels on the vehicle. Go to Pinpoint Test I.
Measure the lateral runout and the radial runout of the front wheels on the vehicle. Go to Pinpoint Test I. Yes
Yes No
No Measure the lateral runout of the front tires on the vehicle. Go to Pinpoint Test I.
Measure the lateral runout of the front tires on the vehicle. Go to Pinpoint Test I. Yes
Yes No
No Measure the radial runout of the front tires on the vehicle. Go to Pinpoint Test I.
Measure the radial runout of the front tires on the vehicle. Go to Pinpoint Test I. Yes
Yes No
No Mark the high runout location on the tire and also on the wheel. Break the assembly down and rotate the tire 180 degrees (halfway around) on the wheel. Inflate the tire and measure the radial runout.
Mark the high runout location on the tire and also on the wheel. Break the assembly down and rotate the tire 180 degrees (halfway around) on the wheel. Inflate the tire and measure the radial runout. Yes
Yes No
No
 Dismount the tire and mount the wheel on a wheel balancer. Measure the runout on both wheel flanges. Go to Pinpoint Test I.
Dismount the tire and mount the wheel on a wheel balancer. Measure the runout on both wheel flanges. Go to Pinpoint Test I. Yes
Yes No
No WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (34 mph) using the speedometer reading, since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Exceeding a speed of 55 km/h (34 mph) or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported can result in tire disintegration or differential failure, which can cause serious personal injury and extensive vehicle damage.
WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (34 mph) using the speedometer reading, since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Exceeding a speed of 55 km/h (34 mph) or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported can result in tire disintegration or differential failure, which can cause serious personal injury and extensive vehicle damage. Spin the front wheel and tire assemblies with a wheel balancer while the vehicle is raised on a hoist. Feel for vibration in the front fender or while seated in the vehicle.
Spin the front wheel and tire assemblies with a wheel balancer while the vehicle is raised on a hoist. Feel for vibration in the front fender or while seated in the vehicle. Yes
Yes No
No WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (34 mph) using the speedometer reading, since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Exceeding a speed of 55 km/h (34 mph) or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported can result in tire disintegration or differential failure, which can cause serious personal injury and extensive vehicle damage.
WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (34 mph) using the speedometer reading, since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Exceeding a speed of 55 km/h (34 mph) or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported can result in tire disintegration or differential failure, which can cause serious personal injury and extensive vehicle damage. Chock the front wheels.
Chock the front wheels. Raise and support the rear end of the vehicle so that the rear wheel and tire assemblies can spin. Refer to Section 100-02.
Raise and support the rear end of the vehicle so that the rear wheel and tire assemblies can spin. Refer to Section 100-02. Engage the drivetrain and carefully accelerate the drive wheels while checking for vibration.
Engage the drivetrain and carefully accelerate the drive wheels while checking for vibration. Yes
Yes No
No WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (34 mph) using the speedometer reading, since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Exceeding a speed of 55 km/h (34 mph) or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported can result in tire disintegration or differential failure, which can cause serious personal injury and extensive vehicle damage.
WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (34 mph) using the speedometer reading, since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Exceeding a speed of 55 km/h (34 mph) or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported can result in tire disintegration or differential failure, which can cause serious personal injury and extensive vehicle damage. Remove the rear wheel and tire assemblies. Refer to Section 204-04.
Remove the rear wheel and tire assemblies. Refer to Section 204-04. Secure the brake drums (if so equipped), by installing wheel hub bolt nuts, reversed.
Secure the brake drums (if so equipped), by installing wheel hub bolt nuts, reversed. Carefully accelerate the drivetrain while checking for vibration.
Carefully accelerate the drivetrain while checking for vibration. Yes
Yes No
No NOTE: Make sure the clutch is the cause of the vibration concern. The vibration should occur during clutch operation. The clutch can also be difficult to engage or disengage. Eliminate all related systems before checking the clutch components.
NOTE: Make sure the clutch is the cause of the vibration concern. The vibration should occur during clutch operation. The clutch can also be difficult to engage or disengage. Eliminate all related systems before checking the clutch components. Yes
Yes No
No Remove the accessory drive belt.
Remove the accessory drive belt. Yes
Yes No
No Check for loose clutch pressure plate bolts. Inspect the clutch pressure plate for damage or for material between the pressure plate and flywheel.
Check for loose clutch pressure plate bolts. Inspect the clutch pressure plate for damage or for material between the pressure plate and flywheel. Yes
Yes No
No Check for worn, broken or loose clutch disc springs.
Check for worn, broken or loose clutch disc springs. Yes
Yes No
No Inspect the clutch disc splines for damage or wear.
Inspect the clutch disc splines for damage or wear. Yes
Yes No
No Check for loose flywheel bolts.
Check for loose flywheel bolts. Yes
Yes No
No Inspect the flywheel surface for wear or damage. Check the flywheel runout.
Inspect the flywheel surface for wear or damage. Check the flywheel runout. Yes
Yes No
No Inspect the transfer case for loose or missing mounting bolts. Check for fluid seepage between the transfer case and the transmission.
Inspect the transfer case for loose or missing mounting bolts. Check for fluid seepage between the transfer case and the transmission. Yes
Yes No
No NOTE: Verify that the driveshaft and pinion flange index marks are aligned.
NOTE: Verify that the driveshaft and pinion flange index marks are aligned. Inspect the U-joints for freedom of movement.
Inspect the U-joints for freedom of movement. Inspect the constant velocity joint for freedom of movement.
Inspect the constant velocity joint for freedom of movement. Check driveshaft runout and, if necessary, check the pinion flange runout.
Check driveshaft runout and, if necessary, check the pinion flange runout. Yes
Yes No
No Measure the rear driveshaft and pinion angles. Refer to Section 205-00.
Measure the rear driveshaft and pinion angles. Refer to Section 205-00. Measure the front driveshaft and pinion angles. Refer to Section 205-00.
Measure the front driveshaft and pinion angles. Refer to Section 205-00. Yes
Yes No
No NOTE: Index mark the driveshaft to the pinion flange and to the output shaft before removal.
NOTE: Index mark the driveshaft to the pinion flange and to the output shaft before removal. Test drive the vehicle.
Test drive the vehicle. Yes
Yes No
No Inspect the output flange for damage.
Inspect the output flange for damage. Inspect the driveshaft constant velocity joints for wear or damage.
Inspect the driveshaft constant velocity joints for wear or damage. Yes
Yes No
No CAUTION: Do not hold the steering wheel against the stops for more than three to five seconds at a time. Damage to the power steering pump will occur.
CAUTION: Do not hold the steering wheel against the stops for more than three to five seconds at a time. Damage to the power steering pump will occur.







