Section 07-01C: Transmission, Automatic, 4R70W | 1996 F-150 (4x2) (4x4) and Bronco Vehicles Equipped with 5.0L Engines Workshop Manual |
Electronic System Description
The powertrain control module (PCM) (12A650) and its input/output network control the following transmission operations:
The transmission control is separate from the engine control strategy in the PCM, although some of the input signals are shared.
The powertrain control module receives some input signals from engine-related sensors:
These signals provide information to the powertrain control module about the load and climate under which the engine is operating. Some other inputs are based on driver inputs, such as accelerator pedal position, which is related to the powertrain control module by the throttle position sensor (TP sensor) (9B989). Still other inputs are provided by:
Using all of these input signals, the powertrain control module can determine when the time and conditions are right for a shift or torque converter clutch application. The powertrain control module can also determine the line pressure needed to optimize shift feel. To accomplish these functions, the powertrain control module controls four electronic solenoids:
The powertrain control module receives and sends electrical signals that are used to make the transmission more responsive to driver and vehicle needs.
The driver demands are transmitted to the powertrain control module through four components:
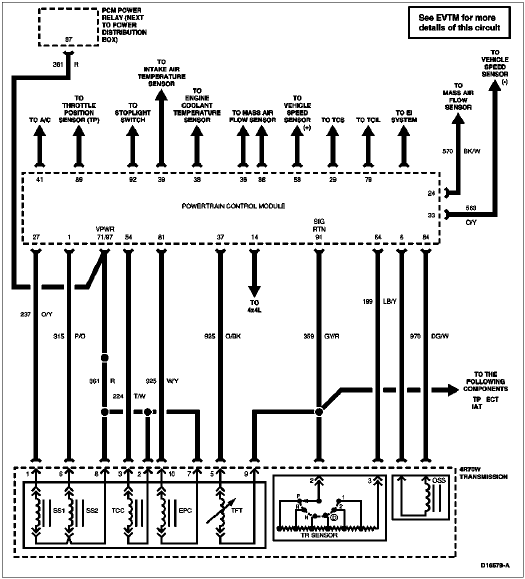
Transmission Electronic Control System Component Locator

| The operation of the transmission is controlled by the powertrain control module. Many input sensors provide information to the powertrain control module. The powertrain control module then controls actuators that determine transmission operation. |
| DTCs: P0603, P0605, P1605 |
 |
| An electromagnetic clutch is energized when the clutch cycling pressure switch closes. The switch is located on the suction accumulator/drier. The closing of the switch completes the circuit to the clutch and draws it into engagement with the compressor driveshaft. When the A/C is engaged, EPC pressure is adjusted to compensate for additional load on engine. |
Symptoms:
|
| DTC: P1460 |
 |
| The brake on/off (BOO) switch tells the powertrain control module when the brakes are applied. The torque converter clutch disengages when the brakes are applied. The switch closes when brakes are applied and opens when they are released. |
Symptoms:
|
| DTCs: P0703, P1703 |
 |
| The engine coolant temperature sensor detects temperature of engine coolant and supplies information to the powertrain control module. The ECT sensor is used to control torque converter clutch operation. The engine coolant temperature sensor is installed into the heater outlet fitting or cooling passage on the engine. For engine control applications, the ECT signal is used to modify ignition timing, EGR flow and air-to-fuel ratio as a function of engine coolant temperature. On electronic instrument clusters, the ECT output is used to control the coolant temperature indicator. |
| Symptoms:Torque converter clutch will always be off, resulting in reduced fuel economy. |
| DTCs: P0117, P0118, P1116, P1117 |
 |
| The electronic ignition consists of a crankshaft position sensor, ignition control module, two four tower ignition coils and the powertrain control module. The ignition control module operates by sending crankshaft position information from the crankshaft position sensor to the ignition control module. The ignition control module generates a profile ignition pickup (PIP) signal (engine rpm) and sends it to the powertrain control module. The PCM uses PIP signal in the transmission strategy, wide-open throttle (WOT) shift control, torque converter clutch control and EPC pressure. |
| Symptoms: Harsh engagements and shifts, late WOT shift, no torque converter clutch engagement. |
| DTCs: P0300 through P0308, P0320, P0340, P1351 through P1364 |
 |
| Description: The low range switch is located on the transfer case cover. It provides an indication of when the 4x4 transfer case gear system is in the LOW range. Modifies shift schedule for 4x4L transfer case gear ratio. |
| Symptoms: Failed on — early shift schedule in 4x2 and 4x4H. Failed off — shifts delayed in 4x4L. If the 4x4 low indicator light fuse is blown, the transmission will shift according to 4x4 low shift schedule regardless of transfer case position. |
| DTCs: P1729, P1781 |
 |
| The intake air temperature sensor provides the sequential fuel injection (SFI) system with mixture (fuel and air) temperature information. The intake air temperature sensor is used both as a density corrector for air flow calculation and to proportion cold enrichment fuel flow. The intake air temperature sensor is installed in the air cleaner outlet tube and provides the fuel system with mixture temperature information. The intake air temperature sensor is used in determining EPC pressure. |
| Symptoms: Incorrect EPC pressure, either high or low, will result in either harsh or soft shifts. |
| DTCs: P0112, P0113, P0114 |
 |
| The mass air flow sensor directly measures the mass of air flowing into the engine. The sensor output is a DC (analog) signal ranging from 0.5 volt to 5 volts used by the powertrain control module to calculate fuel injector pulse width. For transmission strategies, this mass air flow sensor is used for EPC pressure control, shift and torque converter clutch scheduling. |
| Symptoms: High/low EPC pressure, incorrect shift schedule, incorrect converter engagement scheduling and symptoms similar to a throttle position (TP) sensor malfunction. |
| DTC's: P0102, P0103, P1100, P1101 |
 |
| The programmable speedometer/odometer module (PSOM) receives input from the rear brake anti-lock sensor, which is mounted on the rear axle differential housing. The PSOM processes this input signal information and relays it to the powertrain control module and the speed control module. This signal tells the powertrain control module the vehicle speed in miles per hour (mph). The PSOM is also used as an input in determining shift scheduling and electronic pressure control. |
| Symptoms: Harsh engagements, firm shift feel, abnormal shift schedule, unexpected downshifts may occur at closed throttle, abnormal torque converter clutch operation or engages only at wide-open throttle (WOT). May flash transmission control indicator lamp. |
| DTCs: P0500, P1500, P0503, P1501 |
 |
| The transmission control switch (TCS) is a momentary contact switch. When the switch is pressed, a signal is sent to the powertrain control module to allow automatic shifts from first through fourth gears or first through third gears only. The powertrain control module energizes the transmission control indicator lamp (TCIL) when the switch is off. |
| NOTE: TCIL will also flash if the EPC circuit is shorted, or monitor sensor or actuator fails. |
| Sensor: Transmission control switch |
| Symptoms: No overdrive cancel when switch is cycled. |
| DTC: P1780 tested during Key On Engine Off (KOEO) Self Test. |
| Actuator: Transmission control indicator lamp (TCIL) |
Symptoms:
|
| DTC: TBD |
 |
 |
| The throttle position sensor is a potentiometer mounted on the throttle body. The TP sensor detects the position of the throttle plate and sends this information to the powertrain control module as a varying voltage signal. The throttle position (TP) sensor is used for shift scheduling, EPC pressure control, torque converter clutch control. |
| Symptoms: Harsh engagements, firm shift feel, abnormal shift schedule, torque converter clutch does not engage, torque converter clutch cycling. |
| DTCs: P0122, P0123, P1120, P1121, P1124, P1125 |
 |
| The transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor is located on the main control valve body in the transmission sump. It is a temperature sensitive device called a thermistor. It sends a voltage signal to the powertrain control module. The voltage signal varies with transmission fluid temperature. The powertrain control module uses this voltage signal to determine whether a cold start shift schedule is necessary. The shift schedule is compensated when the transmission fluid temperature is cold. The powertrain control module also inhibits torque converter clutch operation at low transmission fluid temperatures and corrects EPC pressures for temperature. |
| Symptoms: Torque converter clutch (TCC) engagement and stabilized shift schedules happen too soon after a cold start. |
| DTCs: P0712, P0713, P1711, P1783 |
 |
| The processor sends a voltage signal to the transmission range (TR) sensor. The TR sensor incorporates a series of step-down resistors that act as a voltage divider. The processor monitors this voltage, which corresponds to the position of the shift lever (P,R,N,D,2,1) and determines EPC pressure. The TR sensor is located on the outside of the transmission on the manual control lever shaft. NOTE: The TR sensor also contains the park/neutral position backup lamp circuits and 4x4L neutral sense circuits. |
| Symptoms: Engagement concerns, wrong gear, no shifts, increase in EPC pressure. |
| DTCs: P0707, P0708, P1705 |
 |
| The output shaft speed (OSS) sensor is a magnetic pickup, located at the output shaft ring gear that sends a signal to the powertrain control module to indicate transmission output shaft speed. The OSS sensor is used for torque converter clutch control, shift scheduling, determining EPC pressure. |
| Symptoms: No converter engagements, harsh shifts, abnormal shift schedules. |
| DTC: P0720, P0721 |
 |
| The electronic pressure control (EPC) solenoid regulates transmission EPC (TV) pressure. EPC pressure is used to control line pressure. |
Symptoms:
|
| DTCs: P1746, P1748 |
 |
| The torque converter clutch solenoid is used to control the apply and release of the torque converter clutch. |
Symptoms:
|
| DTCs: P0743,* P0741,** P1741,** P1742, P1743, P1744** |
| * Output circuit check, generated only by electrical conditions. |
| ** May also be generated by some nonelectrical transmission component condition. |
 |
| Two on/off shift solenoids provide gear selection of first through fourth gears by controlling the pressure to the three shift valves. One unit containing the two shift solenoids is located in the main control valve body. The shift solenoids are two-way, normally open style. |
SS-1 Symptoms: Improper gear selection depending on failure mode and manual lever position.
|
| DTCs: P0750,* P0751,** P0781,** P0782,** P0783,** P1751, P1731,** P1732,** P1733** |
SS-2 Symptoms: Improper gear selection depending on ailure mode and manual lever position.
|
| DTCs: P0755,* P0756,** P0782,** P0783,** P1733,** P1756,P1732** |
SS1 and SS2 Symptoms:
|
| DTCs: P0750,* P0751,** P0755,* P0756 |
| * Output circuit check, generated only by electrical conditions. |
| ** May also be generated by some nonelectrical transmission component condition. |
 |
| Transmission Range Selector Lever Position | PCM Commanded Gear | 4R70W Solenoids | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SS1 | SS2 | TCC | ||
| P/R/N | 1 | ON | OFF | HD |
| (D) | 1 | ON | OFF | HD |
| (D) | 2 | OFF | OFF | EC |
| (D) | 3 | OFF | ON | EC |
| (D) | 4 | ON | ON | EC |
| (D) | ||||
| w/OD OFF | ||||
| 1 | 1 | ON | OFF | HD |
| 2 | 2 | OFF | OFF | EC |
| 3 | 3 | OFF | ON | EC |
| Manual 2 | 2 | OFF | OFF | EC |
| Manual 1 | 1 | ON | OFF | HD |
| 1a | 2 | OFF | OFF | EC |
Transmission Internal Harness

Transmission Vehicle Harness Connector/Harness Diagram

Transmission Vehicle Harness Connectors

| Pin Number | Circuit | Circuit Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 237 (O/Y) | Shift Solenoid No. 1 |
| 2 | 361 (R) | Vehicle Power |
| 3 | 480 (P/Y) | Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Solenoid |
| 4 | — | Not Used |
| 5 | 923 (O/BK) | Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT) Input |
| 6 | 315 (P/O) | Shift Solenoid No. 2 |
| 7 | 361 (R) | Vehicle Power |
| 8 | 361 (R) | Vehicle Power |
| 9 | 359 (GY/R) | Signal Return |
| 10 | 925 (W/Y) | Electronic Pressure Control (EPC) Solenoid |

| Pin Number | Circuit | Circuit Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32 (R/LB) | Starter Control |
| 2 | 298 (P/O) | Fused Run Only Feed |
| 3 | 140 (BK/PK) | Backup Lamp |
| 4 | 33 (W/PK) | Starter Control to Control Module |
| 5 | 57 (BK) | Ground |
| 6 | 199 (LB/Y) | Transmission Range (TR) Sensor to PCM |
| 7 | 359 (GY/R) | Sensor Signal Return |
| 8 | 463 (R/N) | 4x4 Low — Neutral Sense |
Transmission Control System Diagram